Unlocking the Secrets of Dark Matter: How Einstein's Theory Powers NASA's Bold New Telescope
2025-06-17
Author: Noah
A Cosmic Quest Begins in 2027
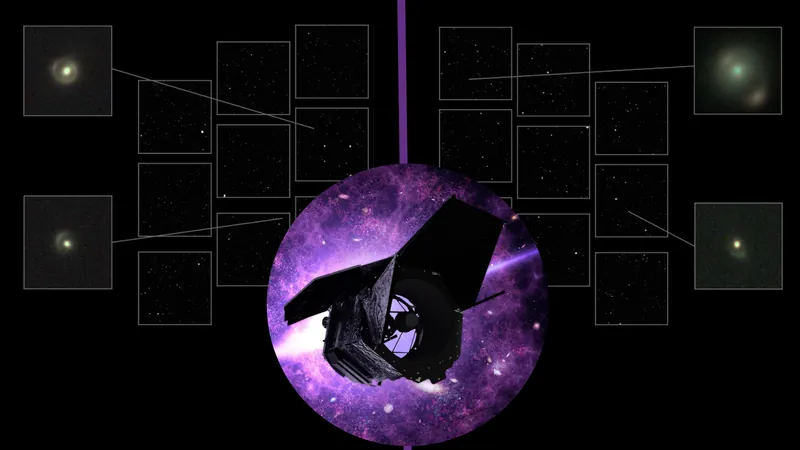
Get ready for a groundbreaking journey into the universe's most enigmatic mystery: dark matter! When NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope launches its science operations in 2027, it will harness a remarkable concept from none other than Albert Einstein. That's right—century-old predictions about gravitational lensing are set to revolutionize our understanding of dark matter.
Einstein’s Vision and Gravitational Lensing Unveiled
Einstein’s general relativity theory suggests that massive objects warp the very fabric of space-time, bending the light emitted from distant galaxies as it passes by these cosmic beacons. This bending will allow the Roman Space Telescope to unveil the hidden mysteries of dark matter by capturing around 160,000 gravitational lenses. researchers believe that approximately 500 of these lenses could illuminate the properties of dark matter, an elusive component accounting for 85% of the universe's mass.
Tackling the Dark Matter Dilemma
Dark matter is as shadowy as it sounds—it doesn't interact with light, making it virtually invisible to current observational technologies. This mysterious substance doesn’t consist of known particles like protons or electrons, which makes detecting it extraordinarily challenging. Scientists have been forced to look beyond the traditional models of particle physics, chasing after new and exotic particles that might constitute dark matter.
Curving Light: Dark Matter’s Subtle Influence
How can dark matter bend light if it cannot be seen? The answer lies in gravity. According to Einstein, all mass causes space-time to curve. This curvature compels light to follow a warped trajectory, allowing dark matter to indirectly showcase its existence through gravitational lensing. This phenomenon can lead to stunning visual effects like Einstein rings or multiple images of the same galaxy.
The Roman Space Telescope: A New Era of Discovery
The Roman Space Telescope promises images 200 times larger and of significantly higher resolution than those from the Hubble Space Telescope. This opens a treasure trove of gravitational lens candidates. Beyond sheer quantity, the telescope’s capabilities will allow scientists to spot smaller gravitational lenses, providing unprecedented insight into the dark matter landscape.
Precision Imaging: A New Standard
Equipped with a cutting-edge 300-megapixel camera, the Roman Telescope will achieve remarkable measurement precision, comparable to detecting the width of a human hair from over two football fields away. This ability is crucial for identifying smaller dark matter clumps that might have contributed to the formation of galaxies.
A Game of Chances in the Cosmic Lottery
Detecting these elusive gravitational lenses is no small feat; it’s akin to winning a cosmic lottery. However, with the Roman Space Telescope, scientists will cast a wide net, dramatically increasing their odds of discovering them. While dark matter itself will remain unseen, its effects can be quantified, providing essential clues to its composition.
Pushing Boundaries in Dark Matter Research
As principal investigator Tansu Daylan eloquently puts it, the mission is clear: to push the limits of what we can observe and leverage every detected gravitational lens to unlock the true nature of dark matter. The Roman Space Telescope is not just a new piece of technology; it's a beacon of hope for revealing the veiled structure of our universe.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)