Unlocking the Secrets of Cognitive Health: How Hemopexin and Muscle Quality Influence Brain Function in Older Adults
2025-05-13
Author: Jacob
Understanding the Link between Hemopexin, Muscle Quality, and Cognitive Function
New research sheds light on the complex relationship between hemopexin levels, muscle quality, and cognitive function among older Japanese adults suffering from cognitive impairment. This groundbreaking cross-sectional study explores how these factors intertwine, particularly focusing on potential differences between men and women.
The Study's Framework
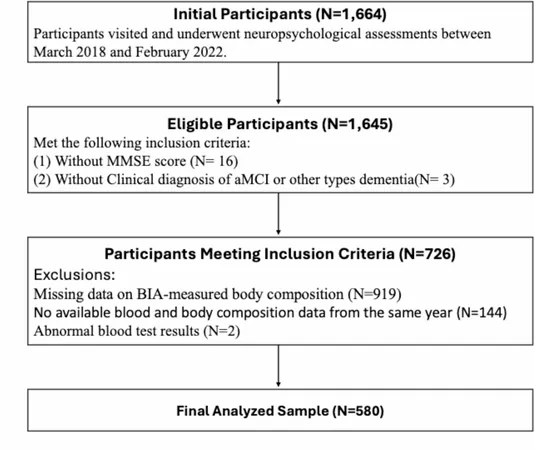
Conducted at the Kyoto Dementia Comprehensive Center, the study involved 580 older adults, aged around 83, who displayed signs of cognitive decline between 2018 and 2022. Researchers assessed cognitive function using the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), measuring hemopexin levels and muscle quality through grip strength and phase angle. Using advanced statistical methods, the study aimed to decipher the connections between these variables and cognitive health.
Key Findings that Could Change Everything
Significantly, higher levels of hemopexin were linked to improved cognitive scores (β = 1.19, p = 0.017), while sarcopenia resulted in a stark decline in cognitive performance (β = -2.28, p < 0.001). What’s fascinating is that men showed a positive correlation with hemopexin's impact on cognition, whereas, in women, sarcopenia had a more pronounced negative effect.
Why Hemopexin Matters in Muscle and Cognitive Health
Hemopexin, a protein crucial for binding heme, has garnered attention for its roles in muscle and brain health. Prior studies suggest that hemopexin may help in clearing harmful substances and could exert neuroprotective effects. Higher levels of hemopexin have been associated with improved cognitive function and reduced Alzheimer's pathology, emphasizing its potential as a biomarker for cognitive health.
Sarcopenia: The Hidden Threat to Cognitive Function
Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and function, not only weakens physical capabilities but has been increasingly linked to cognitive decline. This study affirms previous findings that poor muscle quality correlates with lower cognitive performance, stressing the vital connection between physical and cognitive health.
Personalizing Treatment: The Role of Sex in Cognitive Health
One of the most striking revelations from the study is the role of sex in cognitive function. Men benefitted more from higher hemopexin levels, whereas in women, sarcopenia posed a greater risk, possibly due to physiological differences in how each gender processes iron and responds to oxidative stress. This calls for tailored treatment strategies that consider these differences.
Implications for Elderly Care and Future Research
With dementia being a leading cause of disability in older adults worldwide, these findings underscore the necessity of integrating muscle health into cognitive assessments. Future research should further explore the role of hemopexin as a potential therapeutic target, as well as the sex-specific mechanisms that influence cognitive health. Delving deeper into the interplay between muscle quality, hemopexin levels, and cognitive function could pave the way for groundbreaking advances in elder care.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)