Unlocking the Secrets of Asexual Reproduction: Types, Traits, and Amazing Examples
2025-06-28
Author: Benjamin
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a fascinating biological process where organisms create offspring without the involvement of gametes, or sex cells. This method allows for rapid population growth and ensures the continuation of species in various environments.
Key Characteristics of Asexual Reproduction
The main traits of asexual reproduction include the absence of a mate, genetic uniformity among offspring, and often, less energy expenditure compared to sexual reproduction. This technique is particularly advantageous in stable environments where organisms can quickly proliferate.
Diverse Types of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction comes in several varieties, including binary fission, budding, fragmentation, and vegetative propagation. Each type showcases nature's ingenuity, allowing different organisms to thrive.
Remarkable Examples in the Plant Kingdom
Plants are champions of asexual reproduction. Take the strawberry plant, for instance, which spreads through runners, or the resilient dandelion, which can reproduce via seeds without fertilization. Other notable examples include potato tubers and garlic cloves, both of which give rise to new plants from their existing structures.
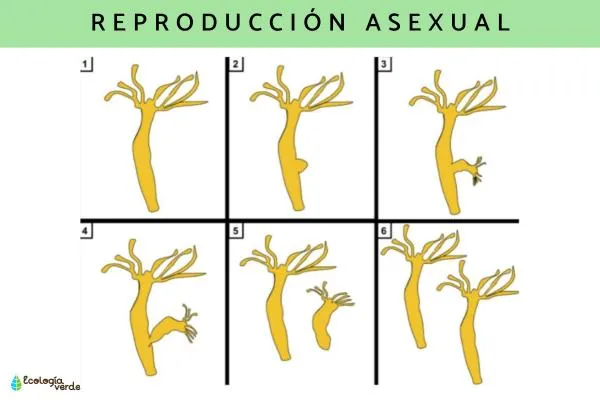
Incredible Instances in the Animal World
Asexual reproduction isn't just limited to plants—many animals exhibit this fascinating trait as well! For example, starfish can regenerate entire limbs and create clones of themselves if a limb is separated. Other creatures like hydras and certain types of worms can also reproduce asexually, making this method extremely effective in various ecosystems.
Conclusion: The Power of Asexual Reproduction
Understanding asexual reproduction unveils the remarkable strategies organisms use to survive and adapt. This form of reproduction highlights the resilience of life, showing us that nature has countless ways to ensure continuity and thrive, even in challenging conditions.









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)