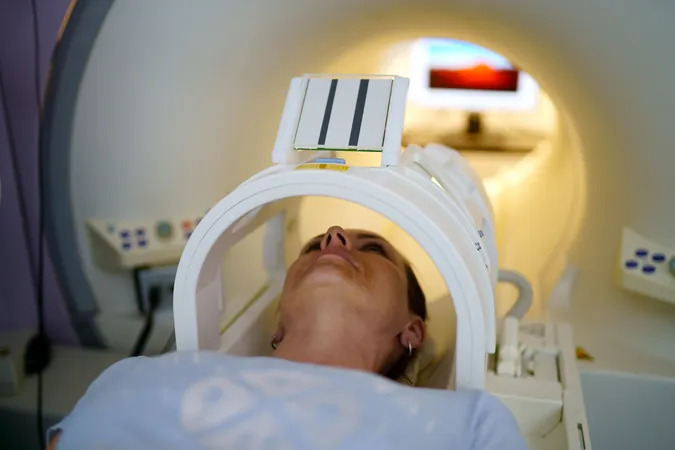
Unlocking the Secrets of Aging: New MRI Scan Predicts Dementia and Disease Risks
2025-07-01
Author: Charlotte
Revolutionary MRI Tool Predicts Aging Rates and Health Risks
In a groundbreaking development, researchers from Duke University, Harvard University, and the University of Otago have unveiled a state-of-the-art tool called DunedinPACNI that can estimate how quickly a person is aging—using just a single MRI scan of the brain. This innovative, non-invasive biomarker has the potential to assess risks for conditions like dementia and chronic diseases, offering a glimpse into a person's health in later years. The findings were detailed in a recent publication in Nature Aging.
Harnessing Longitudinal Data for Future Insights
Developed from the extensive Dunedin Study, which has been tracking the health of over 1,000 individuals born in the early '70s in New Zealand, DunedinPACNI uses nearly two decades of health data. The study monitored various health indicators—ranging from blood pressure to cholesterol levels—enabling researchers to calculate a 'Pace of Aging' score for each participant.
Senior author Ahmad Hariri, PhD, explained the significance: "What's truly remarkable about this is our ability to capture the rate of aging during midlife, which allows us to predict dementia diagnosis in later years."
How DunedinPACNI Works: A Deep Dive into Brain Imaging
Using advanced structural T1-weighted MRI scans from individuals at age 45, the team trained their algorithm to derive an aging score based solely on brain imaging. This powerful tool was then validated against an impressive database of over 50,000 brain scans from various international studies, including the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative and the UK Biobank.
Unique Features: More Accurate than Previous Models
DunedinPACNI distinguishes itself from other aging clocks by relying on longitudinal health data from the same individuals rather than comparing individuals across different age groups. Hariri pointed out that prior assessments could misinterpret various external factors—like exposure to pollutants—as indicators of accelerated aging.
Startling Predictions: Risks Unveiled by DunedinPACNI
When tested on older adults, DunedinPACNI revealed a staggering 60% increased likelihood of dementia development. Participants who scored higher on the aging scale exhibited earlier cognitive decline and significant hippocampal shrinkage. Moreover, the tool predicted an 18% elevated risk of chronic diseases and a alarming 40% higher chance of death in the near future, even among those in seemingly good health.
Broad Applicability and Future Aspirations
The research team affirmed that DunedinPACNI's efficacy is evident across diverse populations, including individuals from low-income backgrounds and non-White groups, suggesting its utility transcends demographic boundaries. This advancement builds on earlier work involving DunedinPACE, a DNA methylation-based aging clock, expanding the range of age assessment to existing MRI data globally.
The authors propose that interventions based on such biomarkers could identify risks for various age-related diseases early, paving the way for timely health interventions that could potentially extend quality of life and longevity.
Challenges Ahead: Need for Diverse Validation
While promising, the study acknowledges some limitations. Most data stems from European adults, which may impede broader clinical applications. Future research is set to validate DunedinPACNI in more diverse groups and explore other imaging techniques to refine its accuracy.
While DunedinPACNI correlates brain structure with health trajectories, it stops short of proving causality, leaving room for further investigation into the complex interplay between brain and overall organ health.
A Glimpse into the Future: What Lies Ahead for Aging Research?
As research progresses, the potential for DunedinPACNI to better inform clinical trials for anti-aging therapies is monumental, allowing for quicker assessments that traditionally would take years to manifest. The journey into understanding aging is just beginning, and DunedinPACNI is paving the way for smarter, more effective health interventions.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)