Unlocking the Future of Healthcare: Introducing the STARD-AI Reporting Guideline for AI Diagnostic Accuracy Studies
2025-09-15
Author: Michael
The Crucial Role of Diagnosis in Healthcare
In the complex world of healthcare, diagnosis is a cornerstone that enables effective treatment and encourages better patient outcomes. Leveraging clinical data from electronic health records, imaging, laboratory tests, and pathology can lead to quicker and more accurate disease detections.
The Challenges in Diagnostic Research
However, the field of diagnostic research is fraught with challenges. Common issues include methodological flaws and a concerning lack of transparency. Inadequate reporting leads to significant misrepresentation in research, resulting in wasted resources. Moreover, diagnostic accuracy isn't a one-size-fits-all characteristic; factors such as clinical context and target populations can significantly alter test outcomes.
STARD: A Solution for Better Reporting
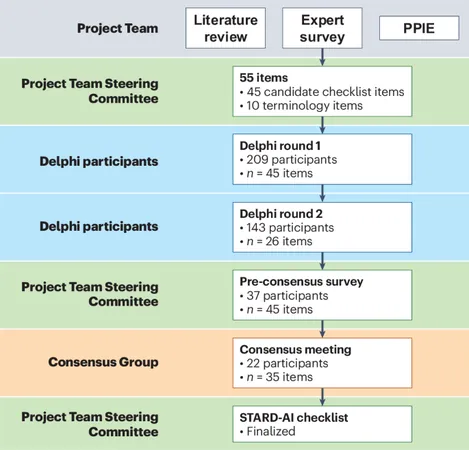
To combat these reporting inconsistencies, the STARD statement was introduced in 2003 and updated in 2015. It provides a standardized framework that outlines 30 essential items every research study should include to improve quality and facilitate better judgment by stakeholders. Compliance with STARD has shown to enhance the thoroughness of diagnostic test reports.
AI: Transforming the Diagnostic Landscape
The release of STARD 2015 coincided with monumental advancements in our understanding of diseases and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI). AI holds transformative potential for diagnostic processes, enhancing both accuracy and efficiency. Despite these possibilities, the integration of AI into diagnostics has progressed without a dedicated reporting guideline that addresses its unique challenges.
Introducing the Game-Changer: STARD-AI
In light of these advancements, the STARD-AI guideline was developed. This comprehensive reporting checklist includes 40 essential items specifically designed for studies evaluating AI diagnostic systems. By establishing minimum criteria, STARD-AI aims to foster transparency, assess methodology robustness, and ensure findings are applicable and generalizable.
What Does STARD-AI Include?
The STARD-AI framework not only modifies some items from the original STARD guideline but also introduces 14 brand-new ones tailored to the intricacies of AI. This checklist covers various aspects, including study methodology and ethical considerations, ensuring vital information is communicated clearly.
Navigating the Unique Challenges of AI
AI brings its own set of complexities, including biases linked to data handling and algorithmic practices. STARD-AI emphasizes these elements, pushing researchers to be transparent about data sources and how patients are selected to mitigate bias. This is crucial for guaranteeing the clinical applicability of AI-driven diagnostics.
Beyond Traditional Diagnostics: The Future is Multimodal
STARD-AI's applicability extends across multiple diagnostic modalities, including imaging and clinical data analysis. The guideline also supports the evaluation of AI models, including large language models, paving the way for more nuanced diagnostic capabilities.
Towards Quality Assurance in AI Diagnostics
By implementing STARD-AI, healthcare researchers can elevate the quality of AI diagnostic studies. The guideline encourages investment in thorough reporting practices, ensuring that essential information is presented for better decision-making by all stakeholders, from healthcare professionals to policymakers.
A Call to Action: Collaborating for Better Outcomes
As AI rapidly advances, embracing reporting guidelines like STARD-AI becomes crucial for maintaining the integrity of clinical trials and diagnostic assessments. The end goal? A healthcare landscape where AI tools enhance diagnostic accuracy without reinforcing existing disparities, fostering equitable and effective healthcare for everyone.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)