
Unlocking the Cosmos: How NASA’s Roman Space Telescope Will Capture Exploding Stars on Film
2025-07-16
Author: Amelia
A New Era in Cosmic Cinema
Prepare for an astronomical revolution! The upcoming launch of NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope promises to transform our understanding of supernovae—those breathtaking explosions of stars that light up the universe. Targeted for launch in just two years, this cutting-edge telescope will orbit at the Sun-Earth L2 point, ready to unveil the mysteries of the cosmos.
Capturing Cosmic Events Like Never Before
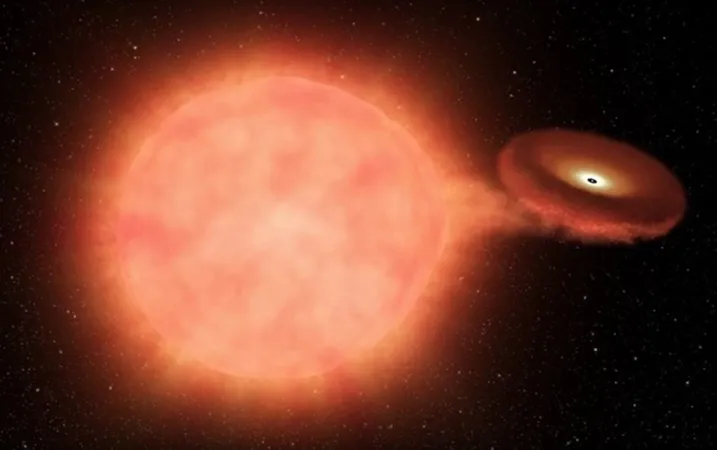
One of the telescope's standout missions is the High-Latitude Time-Domain Survey, which will scan the same region of the sky every five days for two years. The Roman team will painstakingly stitch together these images to create a captivating 'movie' of supernovae, particularly the elusive Type 1a supernovae, which are crucial for measuring cosmic distances.
What Are Type 1a Supernovae?
These celestial bursts occur in binary star systems where a white dwarf siphons material from a companion star. Once the white dwarf reaches critical mass, boom! It triggers a cataclysmic explosion. Unlike core-collapse supernovae, which result from massive stars collapsing into neutron stars or black holes, Type 1a supernovae explode predictably, making them invaluable for astronomers.
A Treasure Trove of Data on Cosmic Expansion
The Roman telescope is set to discover about 27,000 Type 1a supernovae—an astonishing tenfold increase from what we currently know. With this treasure trove of data, cosmologists can delve deeper into the universe's expansion and its enigmatic dark energy.
Trailblazing Insights into Dark Energy
Dr. Ben Rose from Baylor University, who authored a key study on the Roman’s capabilities, states, “Roman will help us understand how dark energy has evolved over time.” This mission opens new paths to comprehend the universe’s expansion and its early history.
Beyond Supernovae: A Wealth of Discoveries Await
The High-Latitude Time-Domain Survey will also explore a variety of transient cosmic events. Its simulations predict an impressive haul, including core-collapse supernovae, kilonovae, and even potential pair-instability supernovae. Each discovery can unlock secrets about black holes, stellar behavior, and the elemental origins of our universe.
Harnessing Cutting-Edge Technology for Spectroscopy
Equipped with advanced instruments, including the Wide-Field Instrument (WFI), Roman will capture and analyze the light from distant cosmic explosions. By dissecting this light, scientists can identify different types of supernovae, advancing our understanding of these spectacular phenomena.
The Hourglass Simulation: Preparing for Discovery
Leading up to its operations, simulations like the Hourglass provide crucial insights into the types of transient phenomena Roman will observe. Anticipating over 64,000 transient objects, the telescope aims to categorize significant cosmic events to better equip scientists for the eventual data deluge.
The Science of the Unpredictable
Every new astronomical mission brings anticipated surprises. Researchers expect the Roman telescope to uncover wonders beyond our current imaginations, with possible new discoveries that could redefine our understanding of the universe.
A Future Undecided: Funding Concerns
Yet, hope is tinged with uncertainty. Recent budget cuts to NASA threaten the Roman's mission, casting doubt on whether it will launch as planned. If its future is secured, the data collected will be a goldmine for astrophysicists, deepening our comprehension of the cosmos—one supernova at a time.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)