Unlocking Health: How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Can Transform Cardiometabolic Health
2025-07-03
Author: Amelia
Revolutionizing Cardiometabolic Care
Cardiometabolic diseases, including heart disease and diabetes, pose a significant global health crisis, contributing to the highest mortality rates in adults. With escalating levels of obesity, hypertension, and insulin resistance, the need for effective management strategies has never been more urgent. Leading health organizations, including the European Society of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, emphasize lifestyle changes— like diet, exercise, and smoking cessation—as critical components for mitigating these health risks.
The Psychological Link to Heart Health
Emerging research highlights a critical yet often overlooked connection between mental health and cardiometabolic disorders. Conditions such as anxiety and depression can exacerbate physical health issues and complicate recovery, leading to higher rates of morbidity and mortality. The urgency for healthcare professionals to screen for and address psychological symptoms among cardiometabolic patients has been underscored by leading health authorities.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: The Game Changer
Among various psychological interventions, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out for its proven efficacy in targeting the psychological aspects of cardiometabolic diseases. Focused on altering negative thought patterns and promoting adaptive behaviors, CBT empowers patients to improved health outcomes by enhancing self-care, adherence to treatments, and reducing emotional distress.
Current Research and Meta-Review Insights
However, the landscape of research regarding CBT's effectiveness in diverse patient populations remains somewhat nebulous. Most meta-analyses have mixed samples that do not differentiate adequately between those with cardiometabolic diseases and other chronic conditions. This often leads to oversimplified conclusions about CBT's effectiveness.
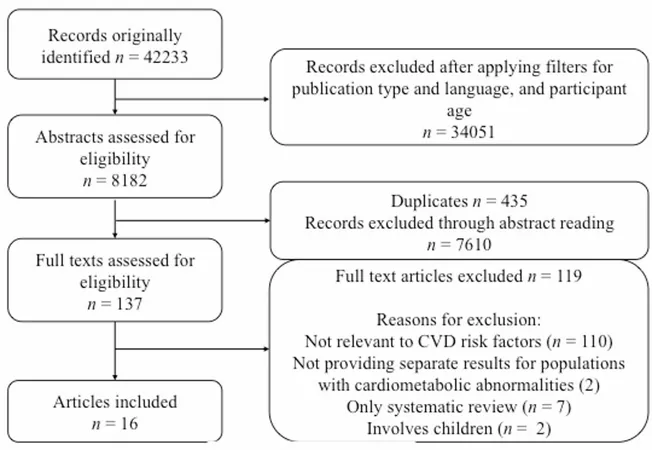
A Comprehensive Analysis
Addressing this gap, the latest meta-review meticulously examined the impact of CBT specifically on various cardiometabolic risk factors, including obesity, anxiety, hypertension, dyslipidemias, and diabetes. The review highlights not only the primary advantages of CBT in managing psychological symptoms but also its potential in influencing physiological parameters such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Results You Can Trust
Out of 16 relevant meta-analyses, a significant number demonstrated that CBT can drastically reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety across various populations, from those with coronary artery disease to diabetes. Additionally, CBT has been linked to improved quality of life metrics, particularly in patients with coronary conditions, while offering a mixed bag of results regarding its impact on physical health indicators.
The Path Forward: Future Research Directions
While the findings are promising, the need for more robust, large-scale studies persists. Future research should concentrate on honing in on the specifics of CBT interventions—like delivery methods and session lengths—to identify the most effective strategies. Furthermore, widespread adoption of technology-based CBT programs could pave the way for more accessible treatment options.
Conclusion: A Beacon of Hope
In summary, the synthesis of current evidence encourages the incorporation of CBT into cardiometabolic treatment plans, providing a holistic approach that addresses both mental and physical health. It’s not just about managing symptoms but empowering patients to reclaim their lives through effective behavioral strategies. As we delve deeper into the integration of psychological care into physical health management, the potential for transforming patient outcomes becomes increasingly tangible.









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)