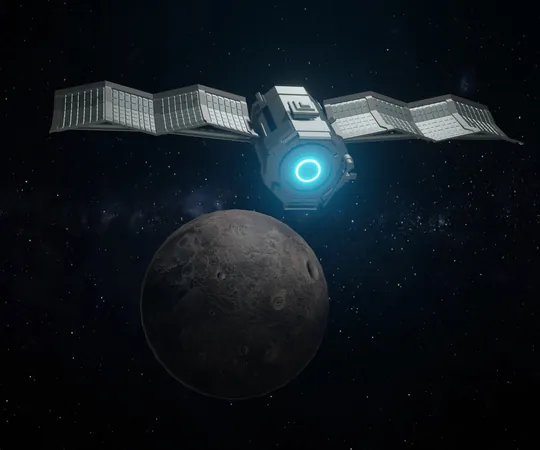

Unleashing the Future: How Electric Propulsion Is Revolutionizing Space Exploration
2025-06-26
Author: Emma
Electric Propulsion: The Game Changer in Space Exploration
Electric propulsion is ushering in a new era of space exploration by transforming electric energy into powerful thrust via advanced ion and Hall-effect thrusters. This technology not only maximizes efficiency and specific impulse but is also the go-to choice for long-duration missions. Noteworthy spacecraft like NASA's Dawn and ESA's SMART-1 have harnessed electric propulsion to execute intricate navigational maneuvers with pinpoint accuracy.
Why Electric Propulsion Matters: A Quick Overview
At its core, electric propulsion is a groundbreaking shift in space technology, converting electric energy into mechanical power through the acceleration of propellants via electrostatic or electromagnetic forces. Ion thrusters shine in this arena, offering remarkable efficiency and specific impulse, especially advantageous for lengthy missions that demand minimal fuel. The integration of solar power enhances this technology's sustainability, enabling spacecraft to operate continuously without traditional fuels. By 2019, over 500 spacecraft had adopted electric propulsion, solidifying its role in modern space exploration.
Ion vs. Hall-Effect Thrusters: The Power Duel
Grasping the differences between ion and Hall-effect thrusters is crucial for understanding their functionality in electric propulsion. Ion thrusters rely on electrostatic forces to accelerate ions, achieving a dazzling specific impulse of around 3,000 to 4,500 seconds, making them ideal for deep-space missions. Meanwhile, Hall-effect thrusters use magnetic fields to ionize propellants, producing thrust levels between 50 and 200 mN and specific impulses of 1,600 to 3,000 seconds. Each system has its strengths, influencing their selection based on specific mission needs.
Trailblazers: Missions Utilizing Electric Propulsion
Electric propulsion is already making waves in crucial space missions, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness. NASA's Dawn spacecraft successfully navigated the asteroid belt using ion thrusters, demonstrating the strengths of electric propulsion in deep space adventures. Meanwhile, the Perseverance rover on Mars is optimized with electric systems to enhance energy management and scientific research. ESA's pioneering SMART-1 mission was the first to employ an ion engine for lunar exploration, paving the way for future innovations.
Rethinking Space Travel: Low Thrust, High Efficiency
The landscape of space travel is evolving, and electric propulsion systems are revolutionizing the principles of propulsion. Unlike traditional chemical rockets, electric thrusters yield continuous low thrust, enabling spacecraft to perform detailed maneuvers over extended durations. Specific impulses can soar to 3,000 seconds, significantly reducing fuel consumption for missions targeting the Moon or Mars. Moreover, harnessing solar energy enhances sustainability, paving the way for intricate space operations outside Earth’s immediate grasp.
Challenges Ahead: Technical Hurdles to Overcome
Despite its many advantages, electric propulsion faces several technical challenges that need addressing for full-scale implementation. Key among these is the demand for robust power sources capable of providing consistent energy across long missions, especially in areas with limited sunlight. Additionally, optimizing the scale and thrust of these systems is vital for deep-space ventures. The lower thrust-to-weight ratio compared to chemical rockets necessitates meticulous mission planning.
Looking Ahead: The Bright Future of Electric Propulsion
While challenges linger, the future of electric propulsion in space is bursting with promise. Technologies like ion thrusters are on the brink of redefining deep-space travel, enabling longer missions with decreased fuel dependency. Initiatives such as NASA’s Artemis program are built around these systems for Moon and Mars exploration, while advancements in materials and energy storage are set to enhance propulsion performance. Collaborative efforts and investment into innovative propulsion research are essential to unlock unprecedented horizons in our quest to explore the cosmos.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)