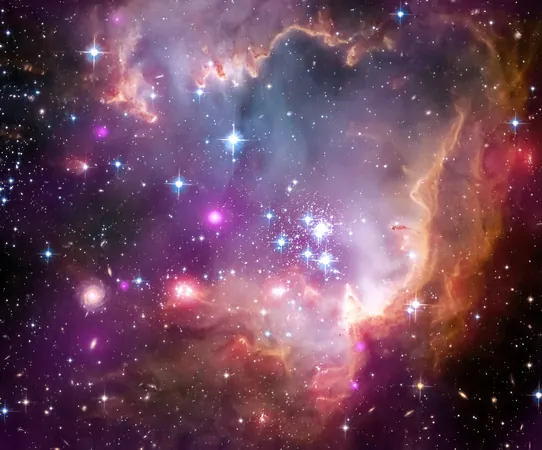

The Small Magellanic Cloud: A Dwarf Galaxy Under Cosmic Strain
2025-05-25
Author: Olivia
Galactic Tug-of-War Explained
The Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), a dwarf galaxy located about 200,000 light-years from Earth, is currently experiencing intense gravitational stress from its larger galactic neighbors. This cosmic drama involves a complex interplay of forces that are stretching and distorting this small galaxy as it orbits the Milky Way.
Revealing Hidden Movements
Recent studies, led by Dr. Kengo Tachihara from Nagoya University, have uncovered fascinating evidence of two distinct stellar movements within the SMC. By analyzing thousands of cepheid variable stars with high-precision data from the Gaia mission, the team discovered that stars closer to Earth exhibit one motion, while those further away show a completely different flow. This innovative approach highlights subtle differences that older methods overlooked.
Mysteries of Gravitational Forces
The gravitational pull of the Large Magellanic Cloud is only part of the story. Dr. Tachihara suggests that the Milky Way’s gravitational field and possibly a past close encounter with the Large Magellanic Cloud are also contributing to the SMC's stretching. This revelation implies a complex galactic ballet, with multiple forces acting on the SMC.
Shattering Old Theories
Historically, astronomers believed that the SMC rotated like a spinning disk. However, new evidence suggests it lacks this significant rotation, challenging previous theories about its dynamics. Ph.D. student Satoya Nakano, the lead author of the study, emphasizes that this calls for new simulations that consider the SMC’s unique behavior, opening doors to understanding how smaller galaxies evolve in the shadows of giants.
Impact on Galactic Evolution
The study of the SMC offers vital insights into galactic evolution. By mapping out how dwarf galaxies like the SMC are influenced by their massive neighbors, researchers can explore how such interactions might ignite or suppress star formation, ultimately shaping the very fabric of the universe.
Future Research Frontiers
Astronomers are eager to compare data from advanced observatories to see if other dwarf galaxies exhibit similar multi-directional movements. Enhanced data surrounding radial velocity will provide clarity on whether different parts of the SMC are indeed pulled in opposing directions, potentially revealing additional hidden influences.
Dynamic Universes in Motion
With ongoing observations, researchers aim to craft large-scale computer models that accurately depict how the SMC has twisted. They hope to identify other dwarf galaxies that might share this similar fate, reshaping our understanding of how these smaller systems interact with larger galactic entities.
Beyond Local Discovery
The implications of this study extend far beyond the SMC. Their findings could offer insights into how early gravitational encounters in the universe set the stage for the evolution of dwarf galaxies. As such, understanding the SMC's complex kinematics becomes integral to piecing together its history with the Milky Way and the overarching narrative of galaxy formation.
A Cosmic Story Unfolding
This groundbreaking study, recently published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, reveals the intricate dynamics of the Small Magellanic Cloud and raises broader questions about how galaxies influence one another across the cosmos. As researchers continue to unveil the mysteries of our universe, the saga of the SMC stands as a testament to the delicate and tumultuous nature of cosmic interactions.






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)