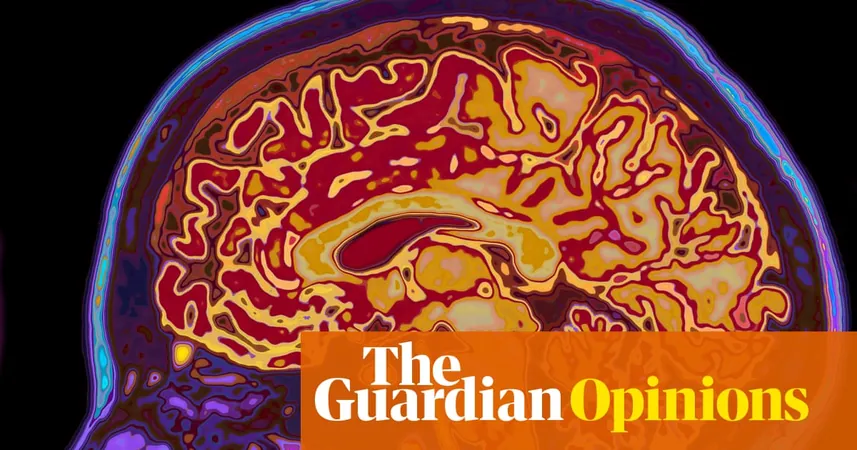

The Looming Dementia Crisis: What You Need to Know and Positive Signs Ahead!
2025-04-08
Author: Emily
Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease and various forms of dementia are alarmingly significant contributors to mortality rates, ranking as the leading cause of death in Britain in 2021, surpassing even COVID-19 and heart disease. In the United States, dementia remains among the top ten causes of death. This complex array of disorders severely damages nerve cells and impairs brain functions, resulting in devastating consequences for individuals and their families. As those affected grapple with confusion and memory loss, the struggle to maintain independence becomes increasingly daunting.
Current Trends and Future Projections
Recent global studies have painted a concerning picture regarding the future of dementia, indicating a potential surge in cases. A notable study published in *Nature Medicine* in January 2025 analyzed the lifetime risk of developing dementia among 15,000 middle-aged U.S. adults and concluded that 42% of individuals over 55 are expected to face this neurological threat. This figure marks a significant rise compared to earlier evaluations and signals a doubling of dementia cases over the next four decades, raising urgent public health concerns as our population ages.
Declining Rates of Dementia Diagnoses
However, amidst these grim forecasts, new data is challenging the narrative of a "dementia tsunami." Research shows that age-specific dementia rates have surprisingly declined by around two-thirds among U.S. adults from 1984 to 2024. This trend has also been observed in other countries, including Sweden, the Netherlands, the UK, and France. Simply put, while the absolute number of dementia cases is increasing due to an aging population, the rate of new diagnoses at any given age appears to be decreasing. This suggests that advancements in healthcare enable people to live longer with cognitive impairment occurring later in life.
Factors Influencing Dementia Rates
While the reasons behind the declining dementia rates remain multifaceted, several hypotheses offer insights. Key factors may include lower smoking prevalence, improved educational opportunities, better management of hypertension, and the early detection of cognitive impairments. Research from *The Lancet Commission* estimates that addressing 14 modifiable risk factors—such as education, hypertension, hearing and vision loss, smoking, obesity, and other lifestyle choices—could potentially prevent about 45% of dementia cases. This underscores the importance of both personal and community efforts in safeguarding brain health.
Advancements in Treatment and Public Health
Over recent decades, strides in understanding these risk factors have led to improved public health policies and educational initiatives. Scientific advancements are equally promising; notable new Alzheimer’s treatments, including donanemab and lecanemab, have shown potential in slowing disease progression. Although caution is warranted given the high cost and possible side effects of these therapies, they represent a forward momentum in the fight against dementia.
Comparative Trends in Other Health Issues
In stark contrast, cancer cases, particularly among younger individuals, are projected to rise sharply. The "birth cohort effect" indicates that successive generations exhibit a higher likelihood of developing certain cancers sooner in life, with colorectal cancer diagnoses for individuals aged 15-39 in G20 countries skyrocketing by 70% between 1990 and 2019. This highlights a troubling imbalance wherein progress against dementia is not mirrored in all areas of health.
Conclusion
As inevitable as aging is, the goal of public health is to prolong wellness as much as possible. While it is true that we all face declining health in some form, concerted efforts in lifestyle changes and scientific advancements yield promising developments in delaying dementia onset. Amidst the escalating dialogue on a potential dementia crisis, it's crucial to cling to the positive strides being made. The battle against dementia may be daunting, but there is hope on the horizon!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)