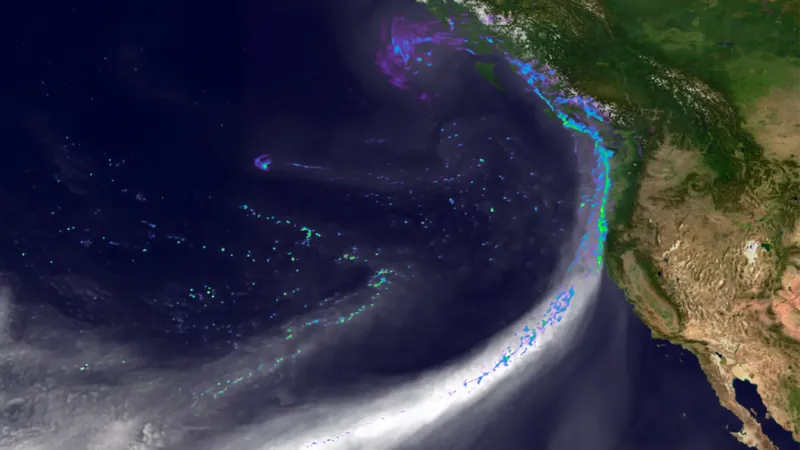

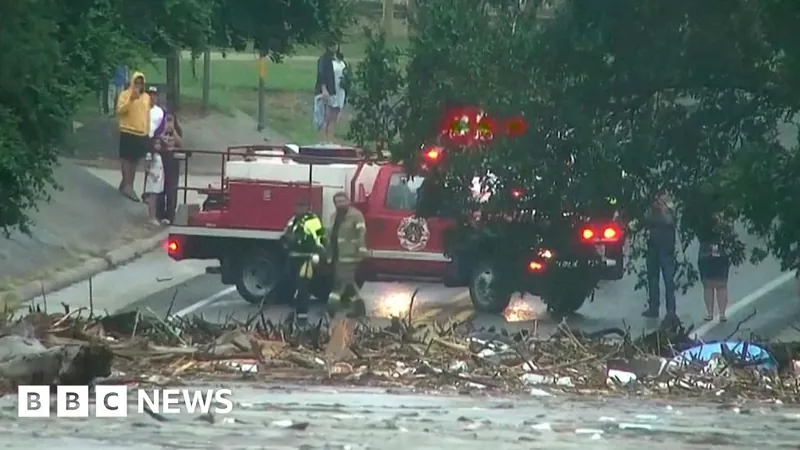
The Hidden Truth Behind Devastating Floods: Scientists Uncover Key Trigger
2025-06-16
Author: Noah
Unlocking the Mystery of Flood Triggers
A groundbreaking study published in the Journal of Hydrometeorology reveals an astonishing link between soil moisture and flooding, analyzing a staggering 43,000 atmospheric river storms across 122 watersheds on the West Coast from 1980 to 2023.
Researchers discovered that wet soils, already saturated from previous rainfall, serve as a primary catalyst for severe flooding. In fact, the study shows that the peaks of flooding can be an alarming 2 to 4.5 times higher when the land is already soaked, explaining why some storms wreak havoc while others merely provide needed rainfall.
The Soil Saturation Spectacle
Lead author Mariana Webb, a Ph.D. candidate at the Desert Research Institute and the University of Nevada, Reno, states, "Flooding isn’t just about storm size; it’s about what’s happening on the land. Pre-event soil moisture plays a pivotal role." This vital research unveils a crucial threshold of soil saturation that dramatically amplifies flood risks.
Mapping the Flood Risk Terrain
The study dives deeper, unraveling the environmental conditions where saturated soils impact flooding most. In arid regions like California and Southern Oregon, storms striking saturated soils are much more likely to trigger floods due to the territory's shallow, clay-rich soils and low water retention.
Conversely, lush areas such as Washington harness deeper soils with significant snowpack, making them more resilient against flooding despite occasional saturation.
Enhancing Flood Predictions: A Top Priority
Webb emphasizes the need for precise flood risk assessments in arid climates where soil moisture fluctuates. Current soil moisture monitoring is sparse compared to rainfall data, limiting accuracy in flood predictions. Increasing real-time monitoring in high-risk watersheds could transform flood management, particularly as atmospheric rivers become more frequent and intense.
Bridging the Gap: Atmospheric Science Meets Hydrology
This research highlights the essential integration of atmospheric science and hydrology to improve flood prediction strategies. Webb collaborated with expert ecohydrologist Christine Albano, focusing on how the interplay between atmospheric conditions and soil moisture can refine our understanding of flood risks.
Albano noted, "By quantifying the saturation point where flood risk spikes, we can leverage advanced weather forecasting to bolster early warning systems. We’re on the brink of revolutionizing how we approach flood management.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)