The Hidden Dangers of Prenatal Stress: How Maternal Depression Impacts Offspring Development
2025-09-14
Author: Sophie
Unveiling the Impact of Prenatal Stress on Offspring Development
New research brings to light the alarming effects of prenatal stress on the development of offspring in wild rodents. With evidence suggesting that maternal mental health can profoundly influence the neurodevelopmental trajectory of their young, this crucial discovery sheds light on why maternal care during pregnancy matters more than ever.
Understanding Prenatal Stress
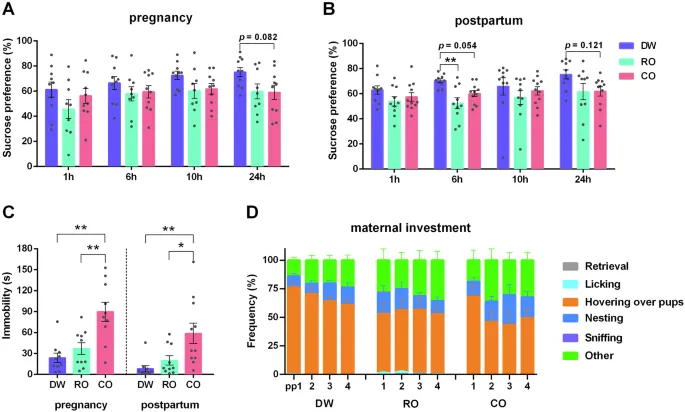
During crucial periods of development, infants are exposed to various environmental stressors. This exposure can be particularly detrimental during pregnancy, where factors such as maternal depression may lead to long-lasting behavioral issues in offspring. Studies have shown that prenatal stress not only affects behavior but also alters neurogenesis, the brain's ability to generate new neurons, which can impact cognitive functions later in life.
The Biochemical Connection
Research indicates that maternal stress changes levels of key hormones and neurotransmitters during pregnancy, which can interfere with fetal brain development. Increased cortisol—a stress hormone—can affect brain regions critical for learning, memory, and emotional regulation, often leading to heightened anxiety, depression, and a host of neurodevelopmental impairments.
Behavioral Consequences in Rodents
In the rodent population studied, exposing mothers to stressors mimicking predation risk resulted in noticeable changes in offspring behavior. These young rodents displayed increased anxiety-like behaviors and impaired social interaction, suggesting that maternal stress can program future behavioral difficulties and emotional challenges.
Epigenetic Changes: A New Concern
The implications of prenatal stress go beyond immediate developmental impacts. Epigenetic modifications—heritable changes that influence gene expression without altering DNA—have been observed in animal models. This means that stress experienced by the mother during pregnancy could affect not just her offspring but potentially future generations.
The Bigger Picture: Implications for Human Health
While the focus here is on rodents, these findings may have significant implications for human health as well. Increased understanding of how maternal stress affects neurodevelopment opens the door for more significant interventions designed to support expectant mothers, potentially reducing the incidence of neurodevelopmental disorders in children.
The Path Forward
Moving forward, prioritizing mental health support for pregnant women may be vital in breaking the cycle of stress-induced developmental issues. Implementing community programs that address maternal well-being and creating awareness around the importance of mental health during pregnancy can be crucial steps in ensuring healthier futures for offspring.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)