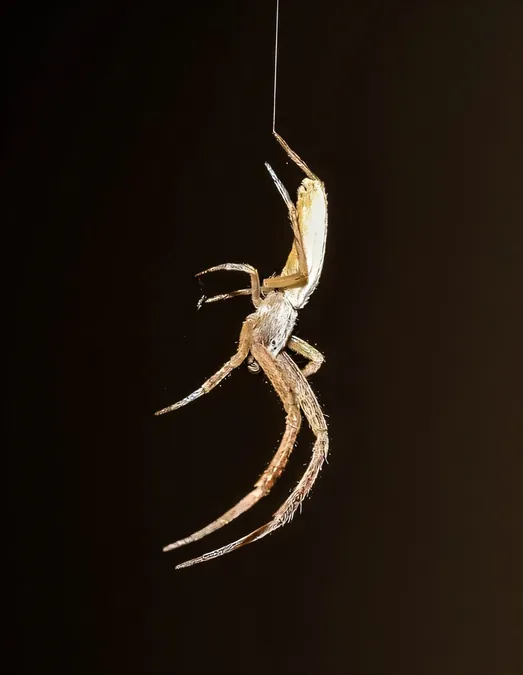

The Feather-Legged Lace Weaver Spider: A Master of Silk and Toxins
2025-06-15
Author: Jacques
Revolutionary Spider Hunting Technique Revealed
A groundbreaking study conducted by researchers has unveiled a fascinating and deadly method employed by the feather-legged lace weaver spider. Unlike most spiders that rely on venom injected through fangs, this unique arachnid kills its prey by ensnaring them in a web of silk and then coating that silk with toxic regurgitated substances.
A Century-Old Mystery Unraveled
This atypical hunting method was first hinted at in a drawing from a 94-year-old scientific paper. The illustration suggested that the feather-legged lace weaver spider not only spun silk but also used toxins to enhance its lethality by wetting the silk. Driven by curiosity, the researchers ventured into greenhouses and plant shops to capture live specimens for detailed examination.
Microscopic Investigation Reveals Surprising Findings
Under the microscope, the researchers made startling discoveries: these spiders did not possess the venomous glands typically seen in their relatives. Instead, peculiar muscle structures took their place, and their fangs contained no injecting mechanisms whatsoever. Digging deeper, the scientists found genes responsible for toxin production were highly active in the spider's midgut.
Deadly Notions: Toxin Testing Unveils Potent Properties
Initial tests confirmed that the toxin was unlike any produced by other spider species. Fascinatingly, when injected into fruit flies, it proved equally lethal, raising questions about the spider’s evolutionary adaptations. Researchers believe the unusual head muscles aid in expelling the potent toxins effectively.
An Evolutionary Leap Forward
Once deemed harmless due to their peculiar anatomy, the feather-legged lace weaver spider now stands as proof that nature boasts varied and ingenious methods of survival. This study not only enhances our understanding of spider evolution but may also inspire future research into innovative toxins for medical purposes. The world of arachnids continues to surprise us!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)