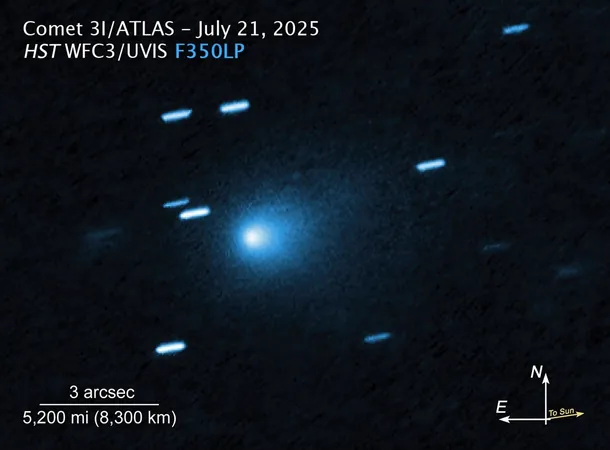

The Fascinating Journeys of Interstellar Visitors: Where Are 'Oumuamua, Borisov, and ATLAS Headed Now?
2025-08-18
Author: Jacob
Three Cosmic Voyagers: 'Oumuamua, Borisov, and ATLAS
In the last decade, astronomers have spotted three incredible interstellar objects (ISOs) passing through our Solar System, igniting intrigue and sparking extensive research. The first, 'Oumuamua, appeared in 2017, a mysterious entity whose nature baffled experts. Next came the comet 2I/Borisov in 2019, and now, we're gearing up for the arrival of 3I/ATLAS, anticipated in July 2025. Sensing the excitement—especially as ATLAS appears to be actively spewing out water vapor near the Sun—scientists are eager to decipher the paths of these intergalactic wanderers.
What Can We Learn from These Interstellar Passengers?
The significance of studying ISOs cannot be overstated. These celestial travelers, remnants from the dawn of planet formation, offer invaluable insights into cosmic conditions beyond our Solar System without the hefty price tag of interstellar missions. Shokhruz Kakharov, a graduate student at Harvard, along with the renowned Prof. Abraham Loeb, has been meticulously calculating their trajectories. Their research unveils unique narratives behind these objects, showcasing they harken from various regions in the Milky Way and span ages from one to several billion years.
Revolutionizing Our Understanding of the Galactic Landscape
The detection of 'Oumuamua launched a celestial revolution, affirming the existence of ISOs and motivating deeper investigations. Kakharov elucidates that, prior to 2017, we lacked empirical evidence that interstellar entities could grace our Solar System. By analyzing these visitors, we glean essential information on the chemistry and structure of exoplanets that can't be sourced through typical observations.
Peering into Galactic Dynamics: A Glimpse into the Past
The Milky Way's evolution tells a tale of diversity and complexity. The study of ISOs reveals not just their origins, but also their implications for understanding stellar populations and even potential source regions of intergalactic materials. Kakharov emphasizes that contexts like the age of 3I/ATLAS—approximately 4.6 billion years—give us profound insight into the dynamics of star formation and evolution across the galaxy.
Utilizing Advanced Simulations for Accurate Trajectories
To dive deeper into this mystery, Kakharov and Loeb employed robust Monte Carlo simulations, examining the galactic potential with the GalPot model. Their statistical analyses yielded strong estimates of the ISOs' future paths, providing clarity amidst uncertainties inherent to long-range predictions.






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)