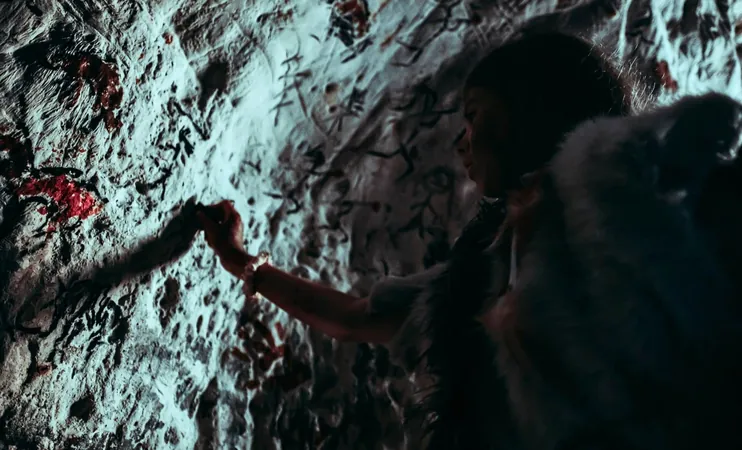

Shocking Revelation: Human Evolution Is a Result of Ancient Genetic Fusion!
2025-05-11
Author: Emma
A Revolutionary Discovery in Human Ancestry!
A groundbreaking study has upended our understanding of human evolution! Scientists now believe that Homo sapiens, long thought to descend from a solitary lineage, actually emerged from an extraordinary genetic fusion between two distinct ancestral populations. This eye-opening revelation, stemming from research by experts at the University of Cambridge and the University of Wisconsin-Madison, prompts us to rethink everything we thought we knew about our origins.
Unraveling the Complex Tapestry of Human History
For decades, the narrative of human evolution suggested a straight path of development, with species evolving independently. However, cutting-edge studies are revealing a more intricate tapestry, with DNA evidence indicating that early humans regularly mingled and interbred with different groups. This astonishing new insight raises crucial questions about which populations contributed to our genetic makeup and how these exchanges have shaped modern Homo sapiens.
The Fascinating Findings: Ancient Genetic Contributions
In a landmark study published in *Nature*, researchers at the University of Cambridge discovered that roughly 20% of our DNA comes from an extinct ancestral lineage, which diverged from another population around 1.5 million years ago. After a long separation, these groups intermingled about 300,000 years ago, a pivotal fusion that sculpted the genetic landscape of contemporary humans.
Introducing the 'Ghost Species' Controversy
Previously, scientists speculated about a so-called 'ghost species'—a mysterious population that ancient humans might have bred with, despite no fossil evidence to support its existence. Recent work from the University of Wisconsin-Madison, led by geneticist Aaron Ragsdale, challenges this idea, suggesting that rather than interbreeding with an unknown entity, ancient human groups regularly split apart and merged back together. This dynamic genetic exchange beautifully explains the rich diversity we observe in today’s humans.
The Impact of Ancient Fusions on Modern Populations
Critical insights from the study highlight two major genetic fusions fundamental to forming present-day human groups. The first fusion, around 120,000 years ago, birthed the Khoisan peoples of southern Africa, whose genetic diversity is unparalleled worldwide. The second, emerging about 100,000 years ago, shaped the populations across Western and Eastern Africa, with some groups eventually migrating beyond the continent. These fusions were likely spurred by drastic climatic changes, including ice ages, which fragmented and then reunited human habitats.
A Paradigm Shift in Human Evolution Understanding
Gone are the days of viewing human evolution as a simple branching tree! New evidence suggests that the evolutionary tree may look more like a complex web, where numerous intersecting paths have created a rich genetic heritage. Early Homo sapiens were not just a homogenous mass; they were vibrant networks of diverse populations engaging in continuous genetic exchanges.
Reinterpreting Ancient Fossils
This fresh perspective complicates our interpretations of ancient African fossils, which exhibit a blend of traits. These fossils, rather than pointing to a 'ghost species,' can now be seen as evidence of early intermingling events. As paleoanthropologist Chris Stringer from the Natural History Museum in London notes, any genetic traces from such ancient encounters would have likely faded over time, reshaping our understanding of our evolutionary lineage.
This stunning research not only redefines our ancestry but also illuminates the beautiful complexity of our genetic story as humans. Are we ready to embrace this new narrative of interconnectedness?








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)