Shocking Revelation: Earth's Magnetic Field Linked to Oxygen Levels!
2025-06-18
Author: Amelia
Every breath we take is rich with 21% oxygen, the essential gas for life. While the crust of our planet has always contained oxygen in its compounds, it wasn’t until approximately 2.4 to 2.5 billion years ago that elemental oxygen began filling our atmosphere, thanks to the industrious cyanobacteria. This monumental event, known as the Great Oxidation Event, fundamentally reshaped Earth's environment.
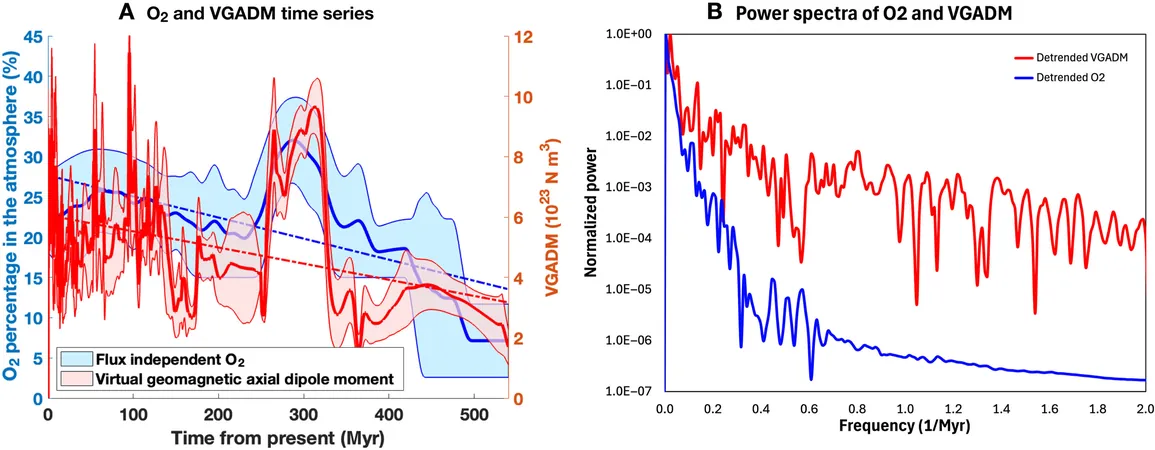
Recent groundbreaking research from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and the University of Leeds has unveiled an extraordinary connection between the strength of Earth's magnetic field and the levels of atmospheric oxygen over the past 540 million years. Astonishingly, measurements indicate that as one rises or falls, so does the other.
This unexpected link could stem from intricate interactions between geological processes deep within Earth, surface redox reactions, and the cycles of life. Published in Science Advances, the study highlights that both the magnetic field and oxygen levels experienced peak intensities between 330 and 220 million years ago.
For years, scientists have speculated on the role of Earth’s magnetic field in fostering a habitable environment. This hypothesis gains further credence through paleomagnetic data that align the existence of the geomagnetic field with the origins of life on our planet. However, direct evidence connecting long-term magnetic field changes and atmospheric oxygen levels has been scarce, largely because traditional Earth system models often ignore the geomagnetic field.
Previous studies suggested that the magnetic field might protect our atmosphere from being eroded by harsh solar conditions, such as high-energy particles from solar winds. Yet, a comprehensive comparison between magnetic records and oxygen levels had not been conducted—until now.
The research team analyzed two independently sourced data sets: paleomagnetic records, documenting the geomagnetic data preserved in rocks, and various geochemical indicators for atmospheric oxygen, encompassing fossilized charcoal and ocean anoxia evidence.
The conclusion? A remarkable correlation of 0.72 between Earth's magnetic dipole and oxygen levels over the last 540 million years, with the most significant alignment showing no time gap between the two records. Even after adjusting for long-term trends, the connection held strong, with only a slight delay of about 1 million years, negligible on a geological scale!
This discovery hints at a profound, previously unrecognized relationship between Earth's deep interior and the ecosystem that thrives on its surface. Not only does it deepen our understanding of Earth’s evolutionary journey, but it also offers essential insights as we search for signs of life beyond our home planet.
Stay tuned for more updates on this fascinating link between geology and the very air we breathe!









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)