Scientists Discover Potential Building Blocks of Life in Nearby Interstellar Cloud — Discover Why This is a Game-Changer!
2024-11-12
Author: Charlotte
Introduction
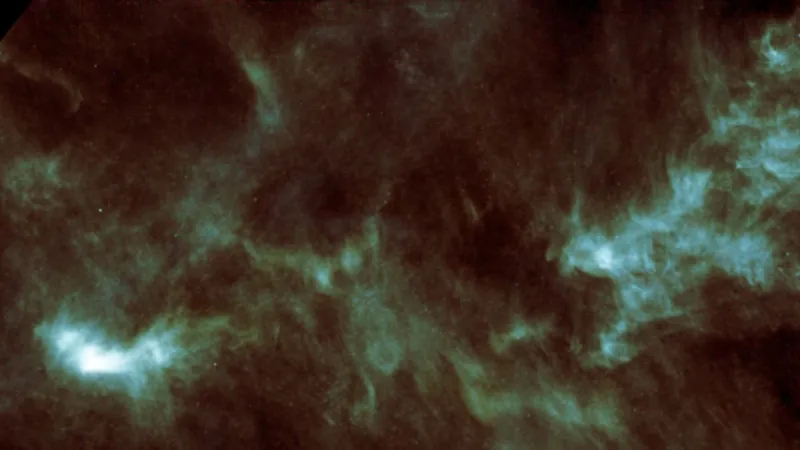
In an exciting discovery that has astrobiologists buzzing, researchers have identified two unique nitrile compounds in the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC-1), one of the closest stellar nurseries to our planet. These molecules, known as malononitrile and maleonitrile, could provide crucial insights into the origins of life beyond Earth.
The Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC-1)
The Taurus Molecular Cloud, located in the constellations Taurus and Auriga, is an area rich in complex chemistry. Utilizing data from the ongoing QUIJOTE line survey conducted with the Yebes Telescope in Spain, scientists have confirmed the presence of these nitrile compounds. Their discovery suggests that intricate chemical processes are happening in the depths of space—processes that might be fundamental in understanding how life originated.
Significance of the Findings
Marcelino Fernández Chico, a researcher at the Instituto de Física Fundamental in Madrid, emphasized the significance of these findings: “Dinitriles, like malononitrile, are seen as precursors to purines and pyrimidines, essential components of RNA and DNA.” This points to the possibility that the building blocks of life may be more widespread in the universe than previously thought.
Thrilling Developments in Astrochemistry
Over the past few years, the field of astrochemistry has entered a thrilling new phase. Advanced observational techniques and innovative telescopes have led scientists to uncover an astonishing variety of complex molecules in space, contradicting past beliefs that interstellar clouds were inert. “Cold interstellar clouds are more than just passive environments; they are active chemical laboratories,” Fernández noted.
Nitriles in Space
Interestingly, nitriles—characterized by a foundational group of carbon and nitrogen atoms bonded in a unique triple bond—are abundant throughout space. Fernández remarked on the remarkable stability of these molecules: “The nitrile group is incredibly stable due to the strength of its triple bond.” This stability, along with their ease of formation, results in a prevalence of nitriles compared to other more fragile molecular types.
Unique Chemistry of Space
Notably, the cold, energy-poor environment of space leads to a different chemistry than what we observe on Earth. In the cosmos, reactions are less about achieving stable outcomes and more about speed and probability. As a result, nitriles often dominate chemical production in interstellar conditions.
Research Findings
To deepen our understanding of how these nitrile molecules formed, scientists analyzed potential precursor molecules, uncovering that malononitrile and maleonitrile were present at lower abundances in TMC-1 compared to similar compounds that contain carbon-carbon triple bonds. Furthermore, it was found that the parent hydrocarbons were about ten times more plentiful than the nitrile radicals essential for the newly discovered compounds.
Challenges in Astrochemistry
While researchers successfully modeled a pathway for maleonitrile's formation, the same couldn't be achieved for malononitrile, highlighting a significant challenge in astrochemistry: new molecular discoveries are rapidly outpacing our current explaining models. In fact, many recently identified molecules, including maleonitrile, are not even cataloged in existing chemical databases.
Future Prospects
Fernández lamented, “The speed at which new molecules are uncovered in space cannot be measured against our chemical models.” However, he also shared optimism, stating that ongoing research efforts are aimed at bridging these knowledge gaps. “The data we’re gathering now will contribute to a better understanding of life’s chemistry across the universe.”
Conclusion
As scientists continue their exploration of the Taurus Molecular Cloud and beyond, the potential implications are vast. Understanding the chemical processes in TMC-1 may give us a glimpse into the cosmic origins of life and could ultimately pave the way for future discoveries of life beyond Earth. This groundbreaking research is just the tip of the iceberg in our quest to answer, "Are we alone in the universe?" Stay tuned for more updates as we delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)