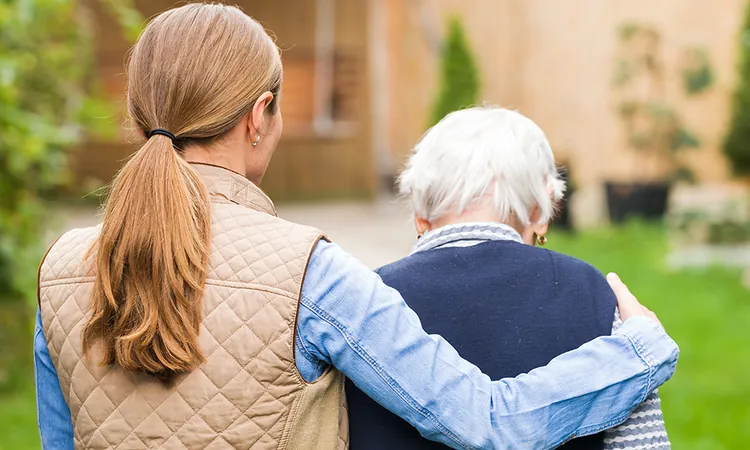

Revolutionizing Support for Dementia: The Compassionate Toolkit for Communities
2025-04-24
Author: Sophie
Transforming Communities for Dementia Support
Living with dementia can often be a lonely journey, filled with barriers like stigma and isolation. However, groundbreaking research from UBC Okanagan is stepping in to change that, aiming to create compassionate, dementia-inclusive communities where connections and support thrive.
Introducing the Compassionate Dementia-Inclusive Communities (CDIC) Toolkit
The new CDIC toolkit serves as a practical guide for organizations eager to provide meaningful support to individuals living with dementia and their caregivers. Dr. Barb Pesut, the project’s principal investigator, highlights the importance of tapping into the existing potential within communities.
"Every community has its strengths waiting to be mobilized," Dr. Pesut explains. "Our mission is to help them recognize and utilize these assets to create real, supportive environments for those affected by dementia."
Key Components of the CDIC Toolkit
This innovative toolkit combines three successful frameworks—compassionate communities, dementia inclusion, and volunteer navigation—into a user-friendly resource designed for community action.
To help organizations foster inclusive environments, the CDIC outlines a structured, six-step process that includes:
1. Building Partnerships
Establish collaborative relationships among local organizations, service providers, and caregivers to address dementia support collectively.
2. Understanding Your Community
By utilizing tools like the Compassionate Dementia-Inclusive Community Index Survey, communities can assess current perceptions and identify areas that need improvement.
3. Preparing Volunteers
The Nav-CARE program offers targeted training for volunteers, ensuring they are equipped to provide top-notch support to those with dementia.
4. Visioning and Implementing a Plan
Communities set clear goals and initiate customized projects, including dementia-friendly arts programs and public awareness campaigns.
5. Evaluating Initiatives
Tailored evaluations allow communities to track progress, celebrate successes, and refine methods for better outcomes.
6. Ensuring Sustainability
The toolkit emphasizes creating long-lasting initiatives through ongoing community engagement, resource sharing, and policy advocacy.
Promising Results from Early Implementations
Six communities across British Columbia, Alberta, Ontario, and Newfoundland have begun implementing the toolkit, with early results showing great promise. Over the coming year, these communities will launch initiatives aimed at fostering inclusion and reducing stigma.
A Vision for the Future
Funded by Health Canada and bolstered by local and provincial organizations, the CDIC project aims to weave compassionate practices into the fabric of community networks. Dr. Kelly Ashford emphasizes the significance of sustainable change.
"This is about building resilient communities where everyone, no matter their health status, feels accepted and nurtured," he asserts.
Empowering Communities to Embrace Inclusivity
The CDIC initiative exemplifies how applied research can improve community welfare. Dr. Pesut underscores the need for community-driven efforts, stating, "We must empower older adults to age in their own homes, surrounded by compassion and meaningful connections."








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)