Revolutionary VR Training Tool Set to Transform Infection Control in Healthcare
2025-06-11
Author: Noah
Groundbreaking VR Initiative Targets Contamination in Medical Facilities
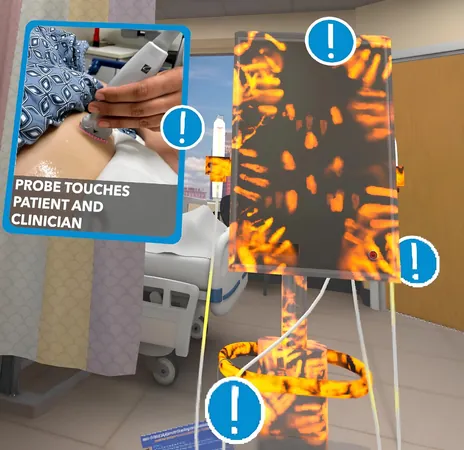
In an innovative leap for infection control, researchers at Mass General Brigham have unveiled a cutting-edge virtual reality (VR) training tool designed to educate clinicians on vital infection control practices. This pioneering tool focuses on the cleaning and disinfecting of portable medical equipment, aiming to significantly reduce the spread of infections in healthcare facilities.
Combatting Healthcare-Associated Infections
Pilot tests of the VR training have been successfully conducted in seven facilities across the United States, with the ultimate goal being to enhance staff competency and safeguard patient safety. According to senior author Dr. Erica S. Shenoy, chief of Infection Control at Mass General Brigham, portable devices—like blood pressure cuffs and ultrasound machines—are frequent culprits in infection spread due to inadequate cleaning.
A Shocking Reality: The Statistics Behind Infections
The severity of the situation is staggering, with healthcare-associated infections affecting 1 in 31 patients, resulting in nearly 100,000 deaths each year and costing healthcare systems over $28 billion annually. Alarmingly, studies reveal that between 25% and 100% of portable medical equipment is found to be contaminated, heightening the need for effective cleaning training.
Immersive Learning Experience Unveiled
The researchers have crafted an immersive VR module that takes users through a simulated inpatient environment using head-mounted displays. This interactive training not only gamifies the learning experience but also visualizes invisible contaminants, allowing clinicians to tackle cleaning procedures for both vital signs and point-of-care ultrasound machines.
A New Perspective on Cleanliness
Dr. Shenoy explained, "We wanted to give clinicians a chance to 'see the unseen' risks, creating an immersive learning environment that translates to real-world skills and knowledge." Feedback from the initial training phase was overwhelmingly positive, with 88.6% of 44 participants expressing satisfaction with the revised module.
Navigating Challenges and Excitement in VR Training
While some participants reported issues like motion sickness and difficulties with handling virtual equipment, the majority embraced the hands-on experience. The project team is now gearing up for further research, moving beyond initial acceptability to rigorously test participants' competencies after VR training.
A Bright Future for Infection Control Training
As Dr. Shenoy stated, "In busy, complex healthcare settings, new training approaches that enhance muscle memory for core infection control practices are essential." Early indications show that when learners engage with enjoyable training methods, their retention and application of important information greatly improve—setting the stage for safer healthcare environments.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)