Revolutionary Neural Network Transforms Space Reactor Shielding Design
2025-04-22
Author: Noah
A Game-Changer in Radiation Shielding
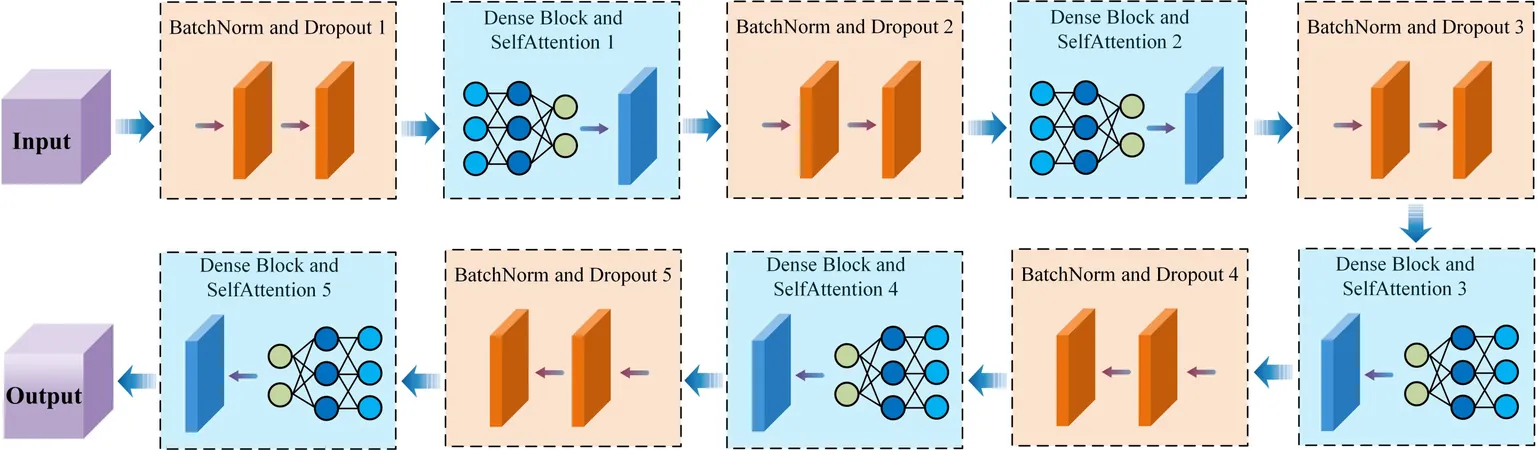
In a groundbreaking development, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have unveiled a cutting-edge neural network model that could revolutionize radiation shielding for space reactors. By utilizing advanced self-attention mechanisms, this innovative model significantly accelerates the design process for shielding configurations crucial for safe space missions.
The Challenge of Compact Reactors
As micro and small reactors gain traction as viable low-carbon energy sources for space exploration, the demand for efficient radiation shielding has never been more pressing. Designing effective shields is complex due to strict weight limits, limited space, and intricate material interactions, making traditional methods less feasible.
Overcoming Limitations of Traditional Methods
While conventional Monte Carlo simulations are incredibly accurate, they are also notoriously slow and resource-intensive. These drawbacks create a significant bottleneck in the design process, especially when rapid iterations are required.
Harnessing AI for Efficiency
To tackle these issues head-on, the researchers turned to artificial intelligence to develop their intelligent model. Trained on datasets generated by SuperMC, a sophisticated radiation simulation tool, this neural network is capable of rapidly assessing various parameters, such as the weight of shielding materials and radiation exposure levels.
Impressive Results
The results are striking: the model's predictions show a deviation of less than 3% compared to traditional Monte Carlo outcomes, yet it requires a fraction of the computational time. This efficiency not only streamlines the design process but opens new avenues for innovation in space reactor technology.
A Bright Future for Space Exploration
With this breakthrough, the future of sustainable and safe energy in space could be on the horizon. By integrating such advanced AI models into their work, scientists can push the boundaries of what is possible in space missions and beyond.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)