Revolutionary Natural Enzyme Transforms Peptide Drug Discovery
2025-08-25
Author: Emily
Unlocking the Future of Medicine
A groundbreaking discovery by researchers from the University of Utah and Sethera Therapeutics has unveiled a natural enzyme that vastly enhances the stability and drug-like properties of peptides. This breakthrough could pave the way for treating diseases previously labeled as "undruggable." Their exciting findings were recently published in the esteemed Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Meet PapB: The Game-Changing Enzyme
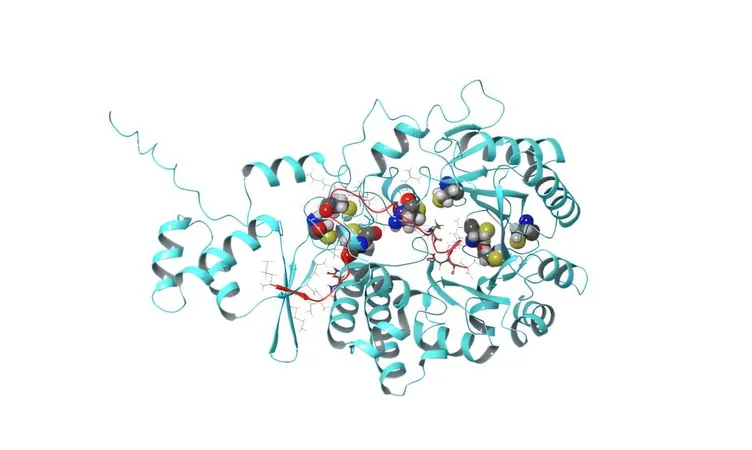
The paper, titled "Diverse thioether macrocyclized peptides through a radical SAM maturase," focuses on the remarkable enzyme PapB. What sets PapB apart is its unique ability to "staple" peptides into circular formations known as macrocycles. This transformation occurs not only with impressive flexibility but also boasts precision, allowing it to work with an array of building blocks, even those typically rejected by biological processes.
Simplifying Complex Processes
Traditionally, peptide drugs depend on disulfide bonds for stability—bonds that can deteriorate inside the body—or rely on convoluted and costly chemical methodologies. PapB revolutionizes this by streamlining peptide synthesis. It produces durable, "stapled" peptides, allowing drug developers to create compounds at unprecedented speeds. The implications are tremendous, as this opens up new avenues for medicines that feature characteristics like enhanced cell penetration and oral bioavailability—two crucial facets for effective therapeutic treatments.
A New Era for Drug Development
According to Karsten Eastman, CEO and Co-founder of Sethera Therapeutics, the goal is to create peptides that possess the advantages of both small molecules and biologics. "This enzyme equips us with a durable thioether 'staple' that can modify a broad range of peptide backbones in a single, efficient step, significantly increasing our capacity to explore hard-to-reach biological targets," he explains.
Transforming the Therapeutic Landscape
PapB's discovery positions it as a versatile thioether ligase, unlocking unprecedented opportunities in peptide drug discovery. Its ability to merge biological selectivity with chemical flexibility provides scientists a powerful tool for forging next-gen peptide therapies aimed at tackling diseases once seen as untouchable. Dr. Vahe Bandarian, a prominent chemistry professor at the University of Utah and co-founder of Sethera Therapeutics, emphasizes the control that PapB offers in its 'promiscuity,' allowing for a single thioether placement that meets precise chemical requirements.
A Promising Future Ahead
Thanks to this innovation, researchers now have access to a simple, one-step method for crafting peptide macrocycles. This technique not only combines the benefits of stability and diversity but also preserves the desirable drug-like qualities essential in modern medicine. As biotech and pharmaceutical teams delve into this new frontier, the potential for cutting-edge treatments where conventional drugs have faltered looks brighter than ever.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)