Revolutionary CsPbBr3 X-Ray Detectors Break Detection Limits!
2025-04-15
Author: Benjamin
A Game-Changer in Radiation Detection!
In a groundbreaking breakthrough, a team of researchers led by Prof. Meng Gang from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has supercharged CsPbBr3-based X-ray detectors, shattering previous detection limits and ushering in a new era of radiation detection technology.
Their remarkable findings, detailed in the renowned journals Applied Physics Letters and Advanced Functional Materials, pave the way for the next generation of X-ray imaging that promises to be both safer and more precise.
Tackling Noise and Sensitivity Challenges!
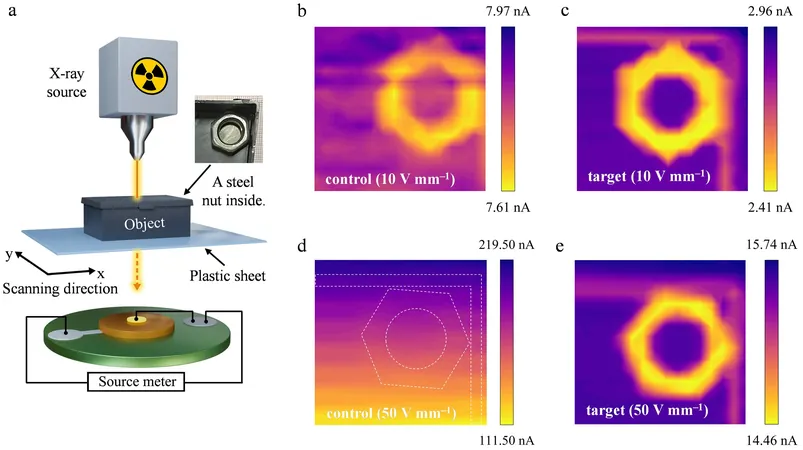
One of the key hurdles encountered with CsPbBr3 in X-ray detectors has been the need to minimize noise while maximizing sensitivity. The innovative team tackled these challenges head-on.
Using a cutting-edge liquid nitrogen cooling technique, they managed to eliminate detrimental deep-level defects in CsPbBr3 single crystals. This remarkable method boosted the material's resistivity by two orders of magnitude and lowered the detection limit to an astonishing 0.054 nGyair·s⁻¹, allowing for the detection of even the faintest X-ray signals.
A Solution for Polycrystalline Wafers!
The team didn’t stop there; they also resolved the issue of ion migration in more practical polycrystalline CsPbBr3 wafers, which are essential for large-scale applications.
In collaboration with Prof. Fang Xiaosheng's group from Fudan University, they developed a remarkable grain boundary passivation method that elevated the ion migration activation energy to 0.56 eV. This innovation significantly curbed dark current drift under high electric fields, allowing the polycrystalline detector to achieve a detection limit of 9.41 nGyair·s⁻¹ while preserving outstanding image contrast.
Changing Lives with Safer Imaging!
These enhanced CsPbBr3 detectors hold the potential to dramatically reduce the radiation dose necessary for X-ray imaging, an especially crucial factor for protecting vulnerable populations such as children and expectant mothers.
This incredible advancement not only charts a clearer path toward future X-ray detectors but also propels radiation imaging technology into an age marked by enhanced safety and unparalleled precision.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)