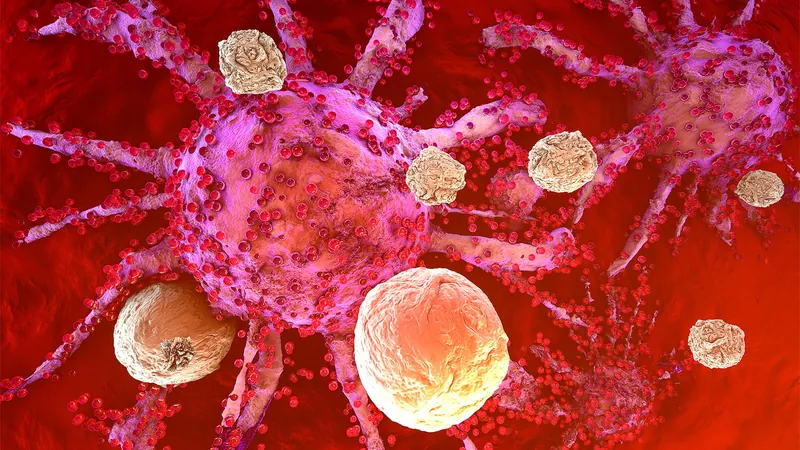
Revolutionary ‘Compound B’: The Game-Changer in the Fight Against Cancer and Chronic Diseases!
2024-09-26
Author: Noah
In an exciting breakthrough, researchers at the University of Alberta have unveiled a groundbreaking molecular compound known as Compound B, which has the potential to significantly enhance immune responses in the battle against cancer and chronic infections. This innovation is generating buzz in the medical community, hinting at a future where small-molecule drugs could redefine immunotherapy and improve patient outcomes.
Professor Khaled Barakat, a key figure in the Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Studies, highlighted that "This is a step forward towards developing a small-molecule drug that can help activate the immune system." With its promise, Compound B is poised to revolutionize how we approach immunotherapy, offering hope to patients struggling with various immunological diseases.
The Advantages of Small-Molecule Drugs
Traditional treatments often rely on immunostimulants, which, while effective, come with a hefty price tag and several drawbacks. These treatments can require high doses and typically have longer half-lives, increasing the likelihood of adverse reactions. In contrast, small molecules like Compound B are not only more affordable but boast a shorter half-life, leading to fewer side effects and enhanced circulation within the body.
One of the most exciting characteristics of Compound B is its ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, offering a unique opportunity to address hard-to-reach tumors that other drugs cannot effectively target. Professor Barakat emphasized, “If you have a small molecule which can cross the blood-brain barrier, you can actually start treating unreachable tumors.”
How Compound B Works
Compound B is derived from another potential compound previously under investigation. The significant advantage of Compound B is its higher water solubility, which is crucial for ensuring that the drug is effectively absorbed and disseminated throughout the body. Initial studies have shown that Compound B can stimulate immune cells, leading to increased levels of T cells—immune cells that play a critical role in identifying and attacking cancer cells—and cytokines, which are vital for regulating immune responses.
Cutting-Edge Research Techniques
The team led by Professor Barakat employs advanced techniques such as machine learning and molecular modeling to identify promising compounds for further testing. "We do everything you would do in an experiment in the lab, but we do it in the computer," he noted, illustrating the innovative approach taken in this research.
After narrowing down potential compounds, they conduct experiments using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), which mimic the immune response of the human body. This enables the researchers to assess how well Compound B activates the immune system.
Looking Ahead
Research into the potential targets for Compound B is currently underway, and the team anticipates publishing more findings in the near future. This interdisciplinary project also involves collaboration with experts from dentistry, chemistry, oncology, biochemistry, and medical microbiology and immunology, reflecting a concerted effort to tackle a significant health challenge. The initiative has garnered support from organizations such as the Alberta Cancer Foundation and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
As Professor Barakat put it, “It is a breakthrough for our group that we’re really happy about, and we hope to follow the same procedure in developing new drugs in the future.”
With its potential to change lives, Compound B might just be the first step toward a new era in cancer treatment and the management of chronic diseases. Keep an eye on this story as researchers continue to unravel the mysteries of this promising new compound!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)