Revolutionary Catalyst Breakthrough: Eradicating Benzene and Toluene Pollution!
2025-08-25
Author: Liam
A Game-Changer in Pollution Control
Researchers at the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences have unveiled a groundbreaking catalyst, MnCoOx, that promises to effectively eliminate two of the most hazardous pollutants: benzene and toluene. This innovation, recently highlighted in the journal Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, marks a significant advancement in our battle against volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in industrial emissions.
Why This Matters?
Benzene and toluene are not just ordinary pollutants; they pose serious health risks and environmental threats. Traditional methods for removing these toxins are often ineffective, especially when multiple VOCs are released at once. This new study addresses these challenges head-on, revolutionizing the landscape of air quality management.
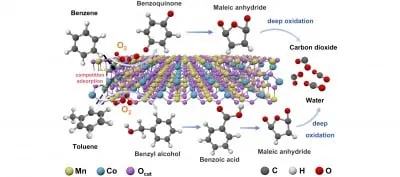
The Catalyst's Superpowers
The research team meticulously crafted the MnCoOx catalysts by altering the ratios of manganese and cobalt. Their findings were astonishing: the MnCoOx and its variant, MnCo2Ox, achieved an impressive 90% conversion rate of both benzene and toluene at temperatures of 290°C and 248°C, respectively. Even more remarkable was the complete degradation of these compounds at elevated temperatures, between 300°C and 350°C. Plus, these catalysts showed a remarkable preference for producing carbon dioxide, indicating their potential for eco-friendly applications.
In-Depth Analysis and Innovations
Through a meticulous series of experiments, the team assessed the performance of their catalysts under different conditions, including both single and multiple VOC scenarios. They employed advanced characterization techniques to delve into the intricate relationship between the catalysts' structure, their redox properties, and catalytic performance.
Implications for the Future
This pivotal research offers a beacon of hope in the fight against industrial pollutants, presenting a viable solution for the simultaneous degradation of benzene and toluene. The outcomes could lead to transformative improvements in industrial emission management and pave the way for the development of more efficient and sustainable air purification technologies.









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)