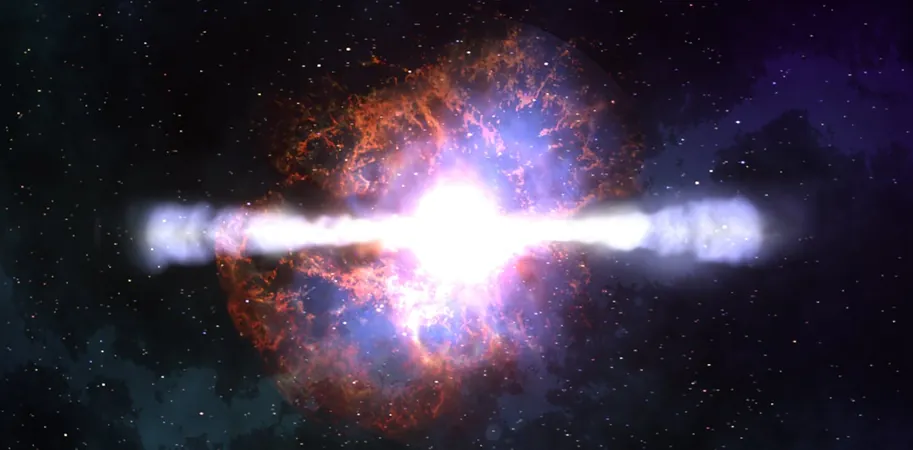

Mind-Blowing Revelation: Could Dark Energy Be a Cosmic Illusion? New Study Suggests a Radical Theory!
2025-01-07
Author: Emma
In a groundbreaking finding that could challenge our fundamental understanding of the universe, a recent study utilizing data from Type Ia supernovas has sparked debate over the existence of dark energy.
Since the late 1990s, astronomers have been grappling with the implications of a universe that is not only expanding but accelerating in its expansion. The prevailing explanation for this phenomenon has been dark energy – a mysterious force thought to make up nearly 70% of the cosmic energy content and serve as a catalyst for the accelerated expansion.
But what if dark energy doesn't exist at all? The new research proposes an alternative explanation known as the Timescape model that rethinks the very fabric of our universe.
What Exactly Is Dark Energy?
Dark energy is a concept central to the current Lambda-Cold Dark Matter (Lambda-CDM) model of cosmology. This model portrays a universe filled with invisible components—dark matter and dark energy—driving the dynamics we observe in the cosmos. According to this view, while dark matter clumps around galaxies and contributes to their gravitational effects, dark energy acts uniformly across space, pushing galaxies apart.
Despite its prominence in cosmological theories, the actual nature of dark energy remains one of physics' greatest enigmas. Various hypotheses have been proposed, ranging from dark energy as an intrinsic property of vacuum energy to the idea of it being a dynamic field evolving over time.
One recent claim from the DESI collaboration indicates that dark energy could even be weakening. This raises questions over whether our current understanding of gravity, dictated by Einstein's theory of general relativity, is wholly adequate for describing phenomena at vast cosmic scales.
Introducing the Timescape Model: A New Paradigm Shift?
The Lambda-CDM model assumes a universe that is homogeneous and isotropic—that is, matter is uniformly distributed across cosmic scales. However, the Timescape model offers a fresh perspective by acknowledging that matter is, in fact, irregularly distributed, consisting of galaxies, clusters, and enormous voids.
According to the Timescape theory, the expansion of the universe is not uniform. Instead, it suggests that the expansion rate differs based on local density. The "void fraction" plays a pivotal role here, indicating the amount of space occupied by expanding voids. These voids, with their lower density, expand more rapidly than areas with higher mass density, creating an average effect that could mimic the accelerated expansion commonly attributed to dark energy.
In essence, the Timescape model proposes that the perceived acceleration of the universe may simply be an illusion shaped by the unevenness of matter distribution.
What Did the New Study Discover?
The study involved an analysis of the Pantheon+ dataset, one of the largest collections of Type Ia supernovas, which has been instrumental as a standard reference for testing cosmological models. The researchers assessed both the Lambda-CDM model and the Timescape model to see which better matched observational data.
Their findings revealed that, particularly for nearby supernovas, the Timescape model provided a more compelling explanation for the data than its Lambda-CDM counterpart. While results showed a statistically significant preference for Timescape, caution must be exercised: potential errors, such as peculiar velocities—random motions of galaxies—and observational biases could skew the analysis.
Moreover, the researchers did not utilize the latest DES5yr dataset, which is known for its consistency and reliability, potentially limiting the robustness of their findings. Other cosmological phenomena—such as baryon acoustic oscillations and gravitational lensing—continue to support the Lambda-CDM model, signaling that further investigations would be needed to fully integrate these aspects into the Timescape framework.
Conclusion: Are We on the Brink of a Cosmic Revolution?
The implications of these findings could be transformative. If the Timescape model gains acceptance, it would necessitate a paradigm shift in our understanding of cosmology and the dynamics of the universe. The notion that the universe’s expansion is an illusion linked to cosmic structure has significant potential to reshape how we perceive reality.
Join the conversation: Could the universe be more enigmatic than we’ve ever dared to imagine? What else might scientists uncover as they probe the depths of the cosmos? Stay tuned, as the next chapter in our understanding of the universe may just be unfolding!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)