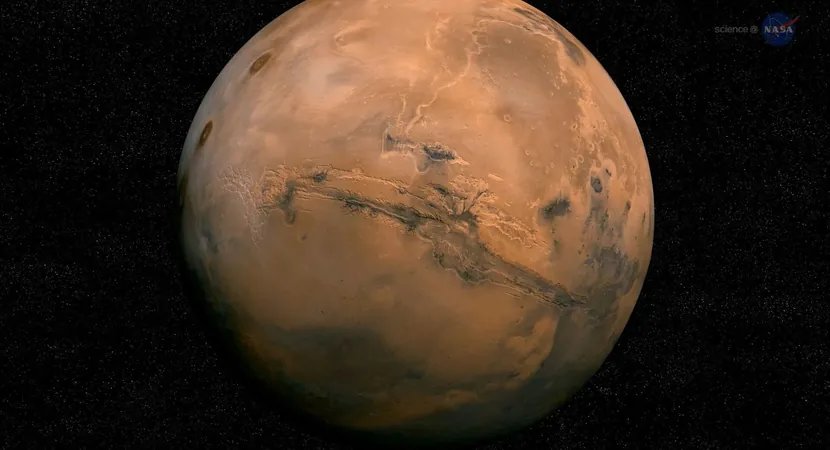

Mars’ Core Revealed: Groundbreaking Discovery Solves a Celestial Puzzle!
2025-09-07
Author: Olivia
An Astonishing Revelation About Mars' Core
In a sensational breakthrough, scientists have concluded that Mars possesses an internal structure akin to that of Earth. Insights from NASA's InSight mission have unveiled that the Red Planet is home to a solid inner core enveloped by a liquid outer core, shedding light on a mystery that has puzzled researchers for years.
What This Means for Mars’ History
This groundbreaking research, published in the journal Nature, is monumental for our understanding of Mars’ evolutionary journey. Billions of years ago, it’s believed that Mars boasted a significantly thicker atmosphere that once allowed liquid water to traverse the surface. This atmospheric protection may have stemmed from a magnetic field similar to Earth’s, which the planet currently lacks.
The Great Atmosphere Loss: How Did It Happen?
Scientists theorize that the disappearance of Mars’ magnetic field led to the atmospheric erosion experienced over eons, transforming the once vibrant planet into a barren desert. In stark contrast, Earth’s robust magnetic field repels charged solar particles, preserving its atmosphere and creating habitable conditions.
A Glimpse into the Core Mystery
Earth’s core is defined by a solid center and a swirling liquid outer core. This convection triggers a dynamo effect, which is crucial for generating the magnetic field. Mars once displayed residual magnetism in its crust, hinting at a similar core structure to Earth. However, experts believe that it cooled and ceased its convective movements long ago.
Evidence of Water: The Old Martian Landscape
The Martian surface is littered with signs of ancient water flow, indicating that it once had more hospitable conditions. From dry lake beds to valley networks etched by ancient rivers, there’s a plethora of geological evidence suggesting a wetter past. Yet, the current Martian atmosphere is thin, leaving little to no water in sight.
InSight Lander's Stunning Discoveries
The Mars lander InSight played an essential role in exploring the Martian core. Initial evidence indicated a liquid core, but subsequent findings from researchers like Huixing Bi of China’s University of Science and Technology suggest the existence of a solid layer within—an exciting twist in the saga of Martian discoveries.
How Mars Compares to Earth: The Core Conundrum
One of the most riveting questions scientists face is whether Mars ever had a core resembling Earth’s. This leads to debates about planetary size and its ability to maintain a protective magnetic field. Could a planet possibly support life if it doesn’t have the right core structure?
Transformative Mars Missions Propel Research Forward
To unravel the enigma of Mars, numerous missions have been launched. NASA’s rovers, along with the European Space Agency's ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter and the MAVEN craft, are all working in tandem to explore various aspects of Mars—from its surface mineralogy to atmospheric dynamics, enhancing our knowledge of its watery past.
The Evolution of Martian Core Models
Stähler's landmark 2021 paper provided key insights into Mars’ core size and density, focusing solely on a liquid core. However, new revelations from Huixing Bi and team indicate a solid inner core, hence stirring discussions within the scientific community rather than igniting controversy. Both studies reflect remarkable progress in Mars research.
Future Investigations: What Lies Ahead?
The recent findings could reshape existing hypotheses and lead to further analyses of InSight data. What other marvels will scientists uncover as they continue to explore the Martian depths? The implications of these ongoing studies extend beyond Mars, providing critical insights into the formation and evolution of celestial bodies throughout our solar system.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)