
Major Breakthrough: Perseverance Rover Spots Signs of Ancient Life on Mars!
2025-09-11
Author: Jacob
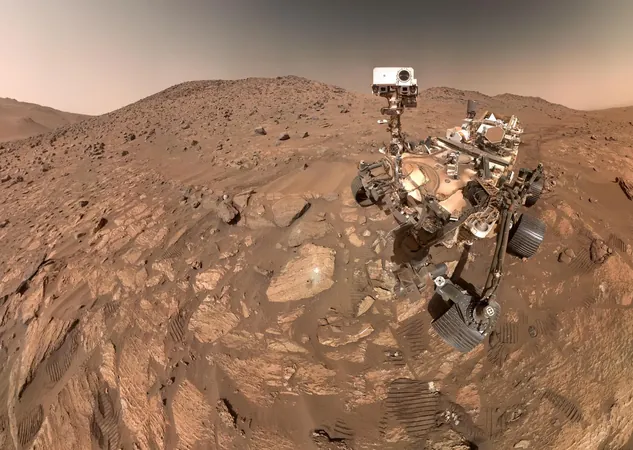
NASA's Perseverance rover has possibly made one of the most groundbreaking discoveries in the pursuit of extraterrestrial life on Mars. A recent analysis of a rock sample from Jezero Crater, aptly named 'Sapphire Canyon,' reveals potential signs that ancient microbes once thrived there!
Drilled from the rocky outcrop known as 'Cheyava Falls' in 2024, this sample boasts chemical signatures that might indicate biological origins—referred to as biosignatures. However, scientists caution that more studies are necessary before reaching definitive conclusions.
Sean Duffy, acting NASA Administrator, expressed excitement over the finding, stating, "This discovery by Perseverance is the closest we've come to identifying life on Mars. A potential biosignature on the Red Planet is a transformative finding that will deepen our understanding of Mars!"
A Promising Location: Jezero Crater
Jezero Crater is an exciting exploration site because it was once home to a massive river delta, which enhances its potential for signs of Martian life. While investigating the 'Bright Angel' formation at the edge of Neretva Vallis, Perseverance discovered Cheyava Falls, an area rich in clay and silt deposited by ancient water flows.
On Earth, these fine sediments are superb for preserving microbial fossils and also contain vital chemical elements that could have nourished early microbial life.
Mystery Spots with Major Implications
Advanced instruments on Perseverance revealed intriguing, colorful patches on Cheyava Falls, dubbed 'leopard spots.' These mineral clusters hint at past chemical interactions, with two materials really catching scientists' eyes: vivianite, typically associated with decaying organic substances, and greigite, which can be produced by microbes.
Their coexistence strongly suggests ancient electron-transfer reactions, a mechanism many microbes use to derive energy. Although these minerals can arise from non-biological processes, the surrounding rocks show no signs of the extreme conditions required for non-living origins.
Young Rocks, New Insights
What is particularly captivating about this discovery is the relatively young age of the examined rocks, compared to other Martian layers previously studied. This challenges the idea that signs of life could only be found in older formations, suggesting that Mars might have been habitable much later in its history than was previously believed.
In fact, earlier evidence of life could be concealed within subtler chemical indicators found in older rock strata.
What's Next in the Quest for Martian Life?
While the findings from Sapphire Canyon are tantalizing, scientists are proceeding cautiously, mindful that ordinary environmental processes could also explain the results. To validate these extraordinary claims, NASA employs rigorous scientific standards for evaluating evidence.
Ultimately, the most definitive insights will likely come when samples collected by Perseverance are brought back to Earth for thorough examination, a mission currently in the planning stages.
A Pivotal Moment in the Search for Life
This discovery accentuates the importance of Perseverance's mission. Every sample, mineral scan, and photograph contributes crucial data in humanity's quest to uncover whether life ever existed on Mars.
If the potential biosignatures from Sapphire Canyon are verified, they could significantly alter our understanding of Mars' history and its timeline for potential microbial life.
As the adventure continues, this groundbreaking discovery stands as one of the most compelling pieces of evidence yet in our age-old quest: Are we really alone in the universe?








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)