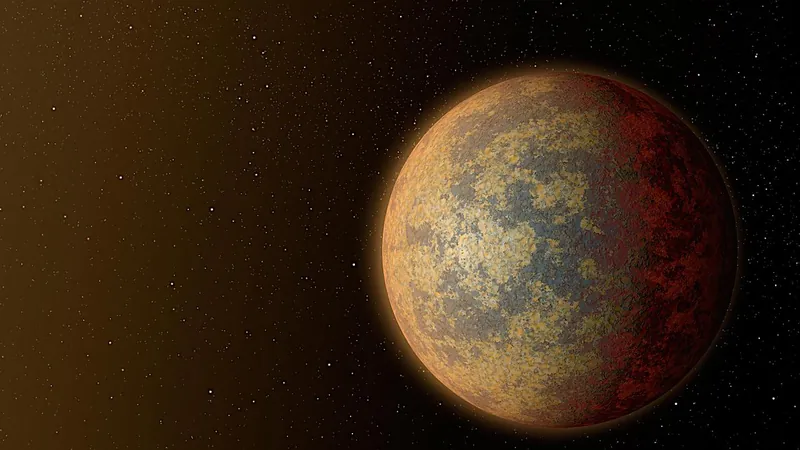

Ignan Earths: The Surprising Potential for Life on High-Heat Rocky Planets
2025-01-11
Author: Olivia
Introduction
Could a rocky planet be too hot on the inside to support life on its surface? A fascinating investigation into this question uncovers the unique potential of terrestrial planets with extreme internal heating, dubbed "Ignan Earths."
The Case of Io
In the universe, few celestial bodies exemplify high internal heating like Io, one of Jupiter's moons. Io boasts a staggering heat flux of approximately 2 W, starkly contrasting with Earth’s mere 90 mW.
The Tidal Venus Limit
But is there a tipping point for internal heat beyond which habitability becomes impossible? Scientists refer to this critical threshold as the Tidal Venus Limit, where geothermal heat surpasses a runaway greenhouse effect of 300 W—a tipping point where conditions could spiral out of control.
Uncharted Territory
Interestingly, the range of internal heating rates between Io and the Tidal Venus Limit remains largely uncharted territory regarding their impact on potential habitability. Recent studies delve deep into the concept of Ignan Earths, investigating how these planets might still foster life despite intense internal heating.
Research Findings
Research indicates that even with substantial internal heating, the mantle of an Ignan Earth can remain predominantly solid. This stability promotes the formation of a buoyant, convective crust capable of creating a viable surface environment.
The Carbonate-Silicate Cycle
The long-term climate conditions on these planets were examined using simulations of the carbonate-silicate cycle under a special tectonic regime called heat-pipe tectonics, expected to be prevalent in such extreme worlds.
Surprising Results
Fascinatingly, the findings reveal that Earth-mass planets with internal heating fluxes below 15 W can maintain average surface temperatures reminiscent of historical Earth conditions, staying below 30°C. Even planets with much higher internal heat fluxes can sustain temperatures significantly cooler than the critical 100°C threshold associated with extreme environments.
Implications for Habitability
The implications of this research are monumental. It expands the search for habitable worlds beyond just Earth-like conditions, implying that the universe may harbor a variety of rocky planets, once thought inhospitable, that could actually support life.
Conclusion
As scientists continue to unravel the mysteries of Ignan Earths, the tapestry of potential habitability across the cosmos becomes ever richer. Stay tuned as we explore how our understanding of life-sustaining environments is evolving, challenging previous beliefs about where we might one day discover extraterrestrial life!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)