Groundbreaking Research Unveils the Secrets of a Vanished Ice Sheet and Its Impact on Sea Levels Today!
2024-11-04
Author: Liam
Introduction
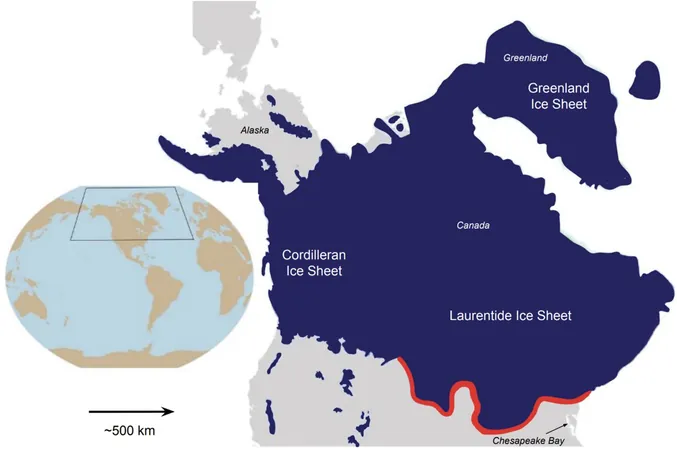
Imagine a colossal ice sheet cloaking Canada and streaming down into a significant portion of the northern United States, much like melted icing cascading down a cake. This was the reality a staggering 19,000 to 26,000 years ago as the ice extended its reach all the way to what we now recognize as Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Michigan, and Wisconsin.
While it's undeniably intriguing to visualize this ancient scenario, what holds paramount importance for us today is the aftermath of the ice sheet’s melt. The melting process didn’t just reshape the land; it ushered in critical dynamics affecting contemporary sea level rise and land subsistence.
Research Overview
Enter Karen Williams, a Ph.D. candidate who embarked on a computational modeling journey to explore how Earth transformed after this ice melted. Together with her advisor, Associate Professor D. Sarah Stamps from the Department of Geosciences, and esteemed collaborators from Italy, including Daniele Melini and Giorgio Spada, they recently published their groundbreaking findings in *Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth*.
Unveiling the Findings: The Rollercoaster of Land Movements
Using advanced computational modeling, Williams scrutinized the repercussions the melting Laurentide ice sheet had on today's vertical land movements. Her investigations ventured into various scenarios examining the ice’s impact on Earth’s surface, oceans, and gravity. This scientific phenomenon is known as "glacial isostatic adjustment," and through nearly 130,000 simulations, they revealed significant insights.
The results painted a clear image: the eastern United States is predominantly experiencing downward land shifts, accelerating relative sea-level rise. In stark contrast, eastern Canada is witnessing an uplifting motion contributing to a drop in relative sea levels.
Decoding the Rising and Sinking Land
Understanding the mechanics behind land rising or sinking has always piqued scientific curiosity and Williams’ models provide indispensable insights. These advanced models pinpoint the factors behind localized vertical movements driven by both natural phenomena and human activities, such as excessive groundwater extraction in regions like the Gulf of Mexico or Chesapeake Bay.
Stamps highlighted a significant revelation: “Some of the most dramatic discrepancies between modeled data and real-world observations emerge in areas known for groundwater extraction, like Houston, Texas.” These findings underscore the urgency of understanding how these dynamics impact communities.
Aiding Community Insight and Planning
But the implications go beyond mere scientific curiosity. The study's results are set to aid in generating maps that will serve researchers and decision-makers alike, guiding aquifer management and providing critical insights into community planning. Ultimately, these research outcomes will feed into a comprehensive report for the U.S. Geological Survey, empowering stakeholders around Chesapeake Bay to navigate the consequential financial, ecological, and social implications of rising sea levels.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as this research continues to shape our understanding of not just our past but also our future in the face of climate changes and rising seas! What other secrets could lie beneath the surfaces we tread upon?









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)