Discovering Tolkien's Legacy: Two New Snail Species Named After Iconic Characters
2024-11-11
Author: Sophie
Introduction
In an exciting revelation for both science and pop culture enthusiasts, researchers have named two newly discovered freshwater snail species from Brazil after beloved characters from J.R.R. Tolkien's legendary "The Lord of the Rings." These unique species, named Idiopyrgus eowynae and Idiopyrgus meriadoci, celebrate the heroism and environmental stewardship exemplified by Éowyn and Meriadoc Brandybuck.
Honoring Tolkien's Characters
The findings were published in the open-access journal *Zoosystematics and Evolution,* where the authors honor Éowyn’s spirit of courage and resilience. The name Idiopyrgus eowynae reflects her defiance against formidable foes like Gríma Wormtongue and the Witch-king of Angmar. Similarly, Idiopyrgus meriadoci pays tribute to Merry's valor alongside Éowyn during the epic Battle of the Pelennor Fields, as well as his pivotal role in rallying nature’s allies, such as the Ents, to protect Fangorn Forest from Saruman’s destructive ambitions.
Habitat and Characteristics
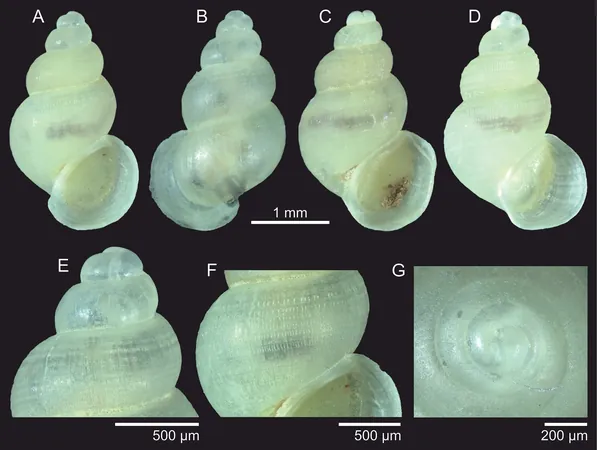
These newly identified snails inhabit a single limestone cave within the Serra do Ramalho karst area of Bahia state in northeastern Brazil. Remarkably, these gastropods belong to the family Tomichiidae, traditionally known for dwelling in surface freshwater environments. Their discovery in a subterranean setting showcases evolutionary adaptability, highlighting how some species can thrive in dark, isolated ecosystems.
Unique Adaptations
Both species exhibit remarkable characteristics, including unique periostracal hairs that resemble thorn-like structures on their shells— a rarity among Brazilian freshwater snails. Their adaptations to life in caves manifest as reduced shell pigmentation, delicate structures, and a diminutive size, ideal for their underground habitat.
Conservation Concerns
The Gruna do Pedro Cassiano cave, the snails' fragile home, faces existential threats from water extraction efforts, rampant deforestation, and the dire consequences of climate change. Given the species’ limited distribution and the precarious state of their environment, researchers advocate for their classification as vulnerable. This discovery not only underscores the richness of Brazil’s subterranean biodiversity but also raises alarms about the broader implications of human activities on these delicate ecosystems.
Conclusion
Dr. Rodrigo B. Salvador, lead author from the Finnish Museum of Natural History, elaborated on his choice of names, stating, “I love to incorporate pop culture references into my research. Just as ancient taxonomists drew from mythology and classic literature, we now embrace contemporary legends. It's a fun way to connect science with the stories that shape our culture.” This innovative approach to naming underscores the ongoing relationship between literature and science, reminding us that even the smallest creatures can carry the legacy of stories that inspire courage and conservation. As we uncover more about these enchanting snails, let us remember the importance of preserving their unique habitats and the biodiversity they represent.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)