
Discoveries from Gaia: The Hidden Webs of Star Clusters in Our Galaxy
2025-08-26
Author: Liam
Revolutionizing Our View of the Cosmos
For over a decade, the European Space Agency's Gaia space telescope has been a game-changer in astronomy, revealing the intricate behaviors and connections of billions of stars. With its remarkable abilities, Gaia has shown that star clusters are far more interconnected than we ever imagined, altering our perception of the celestial tapestry surrounding us.
Gaia's Legacy: A Wealth of Data Yet to Be Unleashed
Launched in 2014, Gaia is now entering a phase of quiet retirement, with a treasure trove of data still awaiting release. However, the initial findings have already delivered unparalleled insights into the positions, motions, and luminosities of stars, offering an enhanced understanding of our galaxy's inhabitants.
Mapping the Milky Way with Precision
Gaia has meticulously tracked the complex journeys of stars, observing phenomena such as 'starquakes,' the cycles of stellar growth and decay, and the unusual paths of intergalactic wanderers seeking refuge in our Milky Way. Its multi-dimensional mapping effort stands as the most detailed and extensive ever created.
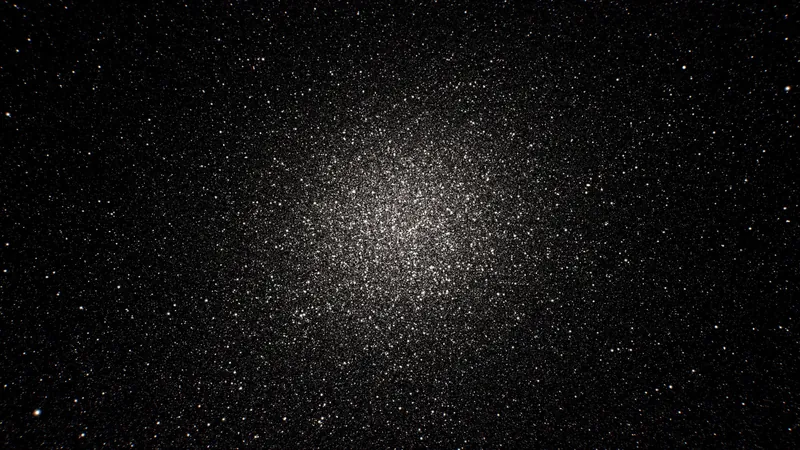
Understanding Star Clusters: A Cosmic Census
Through trillions of observations, Gaia has compiled an extensive catalog of stellar data, encompassing star movements, ages, and more. This colossal dataset offers an unprecedented advantage in our search for understanding star clusters—just a fraction of it has been shared with the scientific community.
The Two Faces of Star Clusters
Gaia has helped define two primary types of star clusters—the smaller open clusters closer to the galaxy's core and the massive globular clusters residing on its outskirts. While many stars originate in these clusters, they often drift apart over time, playing a crucial role in shaping the galaxy's structure and revealing its history.
Artificial Intelligence Meets Stellar Science
Utilizing cutting-edge AI technology, researchers have employed machine learning to identify new star clusters and their members. This innovative approach has led to the discovery of unique star families exhibiting unconventional movement patterns, highlighting how Gaia's detailed data reshapes our understanding of stellar behavior.
Mapping Our Solar Neighborhood
Gaia has transformed our comprehension of the solar neighborhood, crafting detailed 3D and 6D maps revealing the positions, motions, and interstellar materials in close proximity to our sun. These revelations include the structures of dark clouds and clusters where new stars are birthed, unveiling the interconnected nature of nearby cosmic phenomena.
A New Perspective on Star Formation
As Gaia charts the cosmos, it has unveiled fascinating connections among star-forming regions, redefining the interrelationship of gas and stellar formations across vast distances. These insights have shown that gas dynamics and the existing stellar populations significantly influence the star formation process.
Uncovering Tidal Tails: The Mark of Stars' Past
Gaia has illuminated the phenomenon of tidal tails—long streams of stars that signify the historical journeys of star clusters through the galaxy. This groundbreaking research has revealed the complex interactions affecting star clusters, providing vital clues to their origins and evolution.
A Cosmic Revolution Awaits
The Gaia mission represents an astronomical revolution, radically altering our understanding of star clusters and the organization of stars within the Milky Way. Although the telescope has concluded its observational phase, the wealth of data it has produced promises exciting discoveries in the years to come.
Looking to the Future: A Continued Journey
As we anticipate future data releases from Gaia, including more detailed datasets scheduled for 2026 and beyond, the scientific community is poised on the brink of new revelations. This wealth of information will further propel our exploration of the universe, deepening our understanding of the intricate web of star clusters that populate our skies.






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)