Could Axial Seamount Erupt Again? Experts Warn of Possible Volcanic Activity by 2025!
2025-01-02
Author: Emily
Introduction
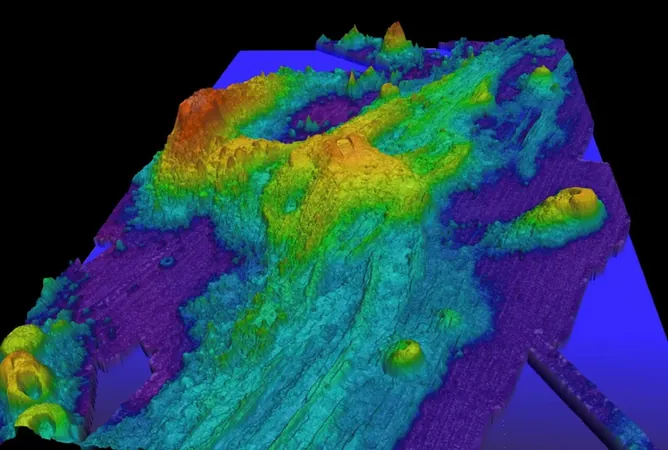
An underwater volcano known as Axial Seamount, located approximately 480 kilometers off the Oregon coast, is stirring with increased volcanic activity, raising alarms among scientists who claim that it could erupt before the end of 2025.
About Axial Seamount
Discovered in 1970, Axial Seamount is one of the youngest and largest underwater volcanoes in the Pacific Ocean. It serves as a crucial research hub, being the site of the world’s first underwater observatory. This facility has been instrumental in helping scientists better understand the behavior and dynamics of volcanic activity beneath the ocean.
Historical Eruptions
Axial Seamount has erupted multiple times since it was first identified, establishing itself as the most active submarine volcano in the Pacific Northwest. The last significant eruption occurred in April 2015, which resulted in thousands of underwater earthquakes and caused the ocean floor around the volcano to sink by about two meters.
Recent Observations
Recently, researchers have noted signs that could point to another impending eruption. A dedicated monitoring blog run by Bill Chadwick from Oregon State University and Scott Nooner from the University of North Carolina at Wilmington has reported concerning developments. As of October 26, 2024, observations indicate that the caldera—the large depression formed after an eruption—has completely re-inflated to levels seen prior to the 2015 eruption.
Seismic Activity
Moreover, there has been an alarming increase in seismic activity, with hundreds of earthquakes detected around Axial Seamount on a daily basis throughout 2024. Although such an eruption may not directly threaten those living on the land, it presents a unique opportunity for scientists to collect invaluable data on underwater volcanic processes.
Uncertainty of Predictions
It’s essential to note that while indicators suggest a potential eruption in 2025, predictions are inherently uncertain due to the complex nature of geological activities. Multiple unpredictable factors can influence volcanic behaviors, much like weather forecasting. Thus, while researchers remain vigilant, they are cautious in making definitive claims about an imminent eruption.
Conclusion
Researchers and enthusiasts alike are keenly watching Axial Seamount, as further activity will not only be critical for volcanic study but could also advance our understanding of underwater ecosystems influenced by such powerful geological events.
Stay tuned for updates, as the situation is still developing!









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)