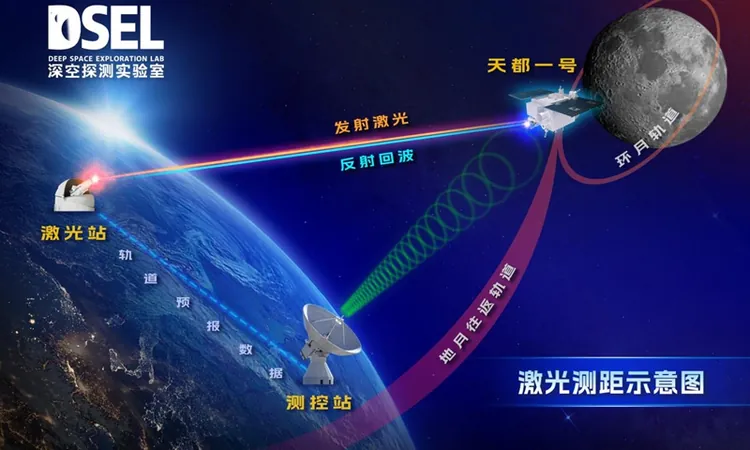
China's Tiandu Satellite Breaks Ground with Daylight Laser Ranging Test
2025-04-29
Author: Olivia
A Revolutionary Leap in Space Technology
In a groundbreaking achievement, China's Tiandu-1 satellite has successfully executed a laser ranging test in the Earth-Moon space, conducting this pioneering feat in broad daylight—a world first! This remarkable advancement marks a significant leap forward in precision measurement technologies in deep space.
Overcoming Nighttime Limitations
Traditionally, satellite laser ranging in the vast expanse between the Earth and the Moon has only been feasible at night, free from the interference of sunlight. This limitation hindered the collection frequency of vital orbital dynamic data. However, the new ability to operate under strong daylight interference vastly expands the observational capabilities of this technology.
Navigating Challenging Conditions
According to the developers at China's Deep Space Exploration Lab (DSEL), performing laser ranging in this environment is akin to pinpointing a single hair from 10,000 meters away — an incredibly challenging task requiring precise tracking and signal acquisition. The successful test not only opens new horizons for data collection but also lays a robust engineering foundation for future applications.
Boosting Future Deep Space Missions
This milestone will play a crucial role in supporting ambitious deep space exploration missions, including the upcoming International Lunar Research Station. As DSEL reported, the implications of this technology extend far beyond mere measurements—they promise to redefine how we explore and understand our solar system.
The Journey of Tiandu Satellites Begins
Launched on March 20, 2024, alongside the Queqiao-2 relay satellite, the Tiandu-1 and Tiandu-2 were crafted as the first satellites by DSEL. After entering their designated circumlunar orbits on March 29 and successfully separating on April 3, these satellites have already begun a series of technological experiments aimed at enhancing lunar communication and navigation capabilities.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)