Breakthrough in Drug Development: Scientists Use Light to Create Essential Compounds
2025-03-24
Author: Noah
Breakthrough in Drug Development: Scientists Use Light to Create Essential Compounds
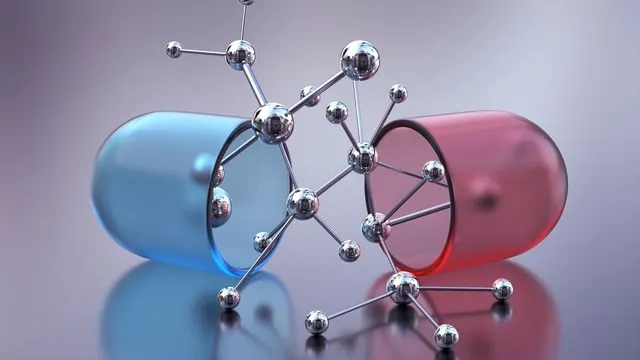
In a remarkable advancement for pharmaceutical chemistry, researchers from Indiana University and Wuhan University in China have revealed a pioneering light-driven chemical process designed to enhance the development of critical drug compounds. Their research, recently published in the journal *Chem*, focuses on the efficient synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinolines, which are essential building blocks in the creation of medications.
These intricate molecules are integral to treatments for a range of serious conditions, including Parkinson's disease, cancer, and cardiovascular disorders. Tetrahydroisoquinolines appear in widely used medications such as pain relief drugs and treatments for high blood pressure. Moreover, they can be found in various natural resources, including certain plants and marine life.
Historically, the synthesis of such compounds has been constrained by conventional methods that often utilize harsh conditions. The innovative approach laid out in this study, co-authored by Indiana University’s Kevin Brown and Wuhan University’s Xiaotian Qi, Wang Wang, and Bodi Zhao, sets a new precedent.
Harnessing Light: A Game-Changer in Chemistry
By employing light as a catalyst, the researchers have introduced a method called photoinduced energy transfer, which initiates a controlled reaction between sulfonylimines and alkenes, leading to the formation of targeted tetrahydroisoquinolines. This revolutionary technique enables the construction of complex molecular structures previously deemed challenging to create, thereby revolutionizing the traditional synthesis landscape.
Professor Brown explains, “Using a light-activated catalyst allows us to execute reactions without depleting the catalyst itself, unlike older methods that necessitate extreme temperatures or strong acids. Imagine cooking with a blowtorch instead of a regular stove—it can inadvertently cause unwanted reactions. Our method avoids these pitfalls by using light to access new energy states, rendering the process cleaner and more efficient.
The team discovered that even minor adjustments to electron arrangements within the reactants significantly influenced the reactions—like puzzle pieces that need to fit perfectly. These precise modifications ensure the desired compound is produced, a critical factor in medicinal chemistry, where structural errors can render medications ineffective or harmful.
Revolutionizing Medicine and Beyond
"This method expands the repertoire of tetrahydroisoquinoline-related compounds that medicinal chemists can explore," Professor Qi highlighted. With certain illnesses having limited therapeutic options, this new process has the potential to accelerate the discovery of effective drugs for challenging diseases such as Parkinson's and various cancers.
The impact of this research extends beyond the pharmaceutical realm. Agriculture could benefit, as similar reactions might help develop advanced pesticides and fertilizers. Furthermore, in materials science, this breakthrough could lead to the creation of innovative synthetic materials with enhanced durability and thermal resistance, catering to industries like aerospace, automotive, electronics, and healthcare.
Looking forward, the researchers aim to refine their reaction techniques further by experimenting with different components and optimizing conditions. They are also keen on collaborating with pharmaceutical companies to explore the practical applications of their method in actual drug production, potentially yielding groundbreaking medications that could transform patient care globally.
“This development equips chemists with a formidable new approach,” concluded Professor Brown. “We are particularly excited about its potential to unlock new and improved therapies for patients worldwide.”
As research in photochemistry progresses, transformative advancements like this promise to reshape the methodologies of medicine and chemistry, heralding a future of faster, safer, and more efficient drug manufacturing processes. Stay tuned for the exciting developments that could soon redefine the possibilities in drug discovery!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)