
Beneath the Crumbling Surface: What a Crater on Mars Reveals About Its Past
2025-06-08
Author: Emma
Mars Mystery Unfolds in Deuteronilus Cavus
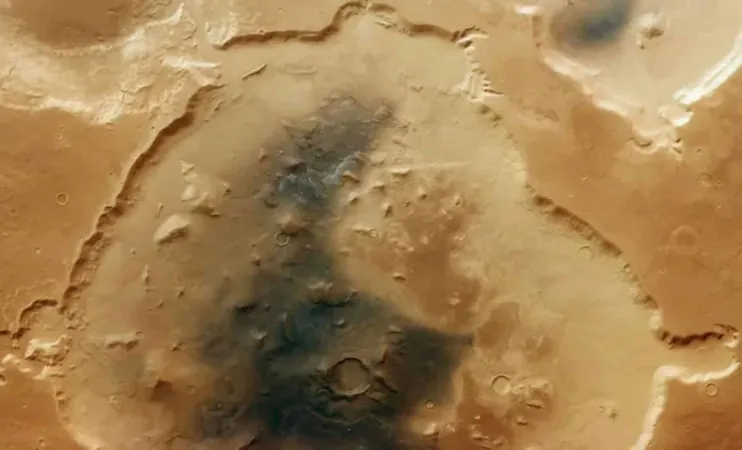
A stunning capture by the European Space Agency's (ESA) Mars Express orbiter is shedding light on a fascinating, eroding crater known as Deuteronilus Cavus. Stretching a vast 75 miles (120 kilometers) across, this crater is situated at the crossroads of Mars' jagged southern highlands and its smoother northern plains.
Unlocking the Secrets of Martian History
The image, taken in October 2024 with the High Resolution Stereo Camera, reveals a dramatically transformed landscape. Scientists estimate that Deuteronilus Cavus was born from a massive impact event between 4.1 and 3.7 billion years ago, a time when Mars, along with its planetary neighbors, faced a deluge of asteroids and comets. Over the eons, the crater has been reshaped by volcanic activity, water erosion, glaciation, and relentless winds.
ESA describes this crater as "soaked in layers of Martian history," highlighting how its formation was influenced by ancient lava flows, liquid water, and multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Now, nearly twice its original size, it serves as a miniature archive of Mars' geological evolution.
Clues to Ancient Water and Volcanic Activity
Among the most exciting discoveries within Deuteronilus Cavus is the presence of clay minerals, suggesting past interactions between volcanic materials and water. This raises tantalizing possibilities about a potentially habitable environment on Mars long ago. Channels carved into the crater's rim hint at ancient water flows, indicating the collapse of what may have been an underground reservoir.
ESA also points out unique grooves and glacial remnants, stating, "these linear grooves indicate where boulders frozen into glaciers were dragged along, carving out the troughs we see today." These formations are strong indicators of previous ice ages, possibly resulting from periods when Mars’ axial tilt was significantly different.
A Look at the Crater's Fascinating Landscape
The interior of the crater features an intriguing mix of rocky knobs, mesas, and plains, interpreted as remnants of a once-prominent central peak that has now collapsed. Much of the crater floor is blanketed in dark volcanic ash, signaling an active volcanic history, while surrounding wrinkle ridges suggest ancient lava flows hidden beneath a cloak of Martian dust.
The diversity and intricacy of features within Deuteronilus Cavus make it a prime target for researchers aiming to decode Mars' environmental past. As ESA officials aptly put it, this "feature-rich crater" showcases the planet’s most dynamic geological processes and offers an enticing glimpse into its complex history.
Stay Updated on Mars Exploration!
Curious about what lies beyond our world? Subscribe to our free newsletter for captivating stories, exclusive updates, and the latest news from the cosmos!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)