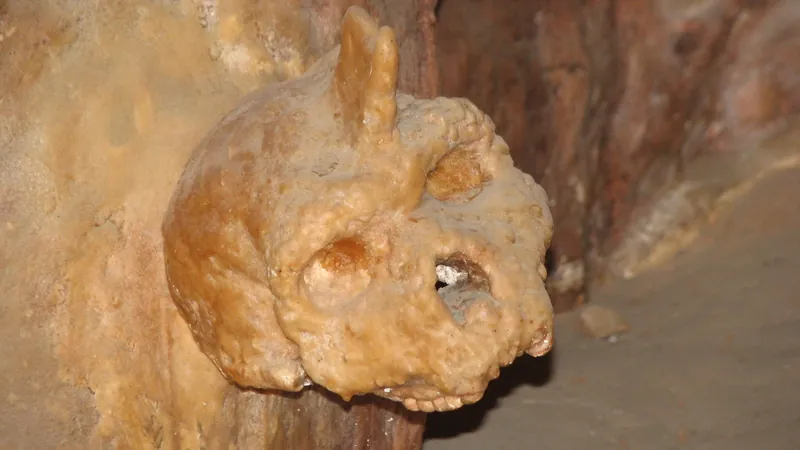

Ancient Skull Unearthed in Greece Now Linked to Rare Human Species After 65 Years
2025-08-31
Author: Noah
A Mysterious Discovery from the Past
Imagine stumbling upon a relic that could rewrite the narrative of human evolution! In 1960, a villager in Greece made such a discovery when he found the Petralona skull embedded in a cave wall near Thessaloniki. This nearly complete cranium has puzzled scientists and evolutionary theorists for decades due to its unique characteristics that don’t fit neatly into our established categories of human ancestry.
An Evolutionary Enigma Awaits Unraveling
As scientific understanding of evolution has progressed since Darwin's groundbreaking work, the Petralona skull has stood out as a significant puzzle. Unlike Homo sapiens or Neanderthals—our well-known ancestors—the skull has been classified as a separate entity, prompting questions about its species identity. What does this mean for our understanding of early humans who once roamed the Earth?
Dating the Skull: A Controversial Journey
The age of the Petralona skull is a hotbed of debate; estimates have varied widely from 170,000 to 700,000 years old! Early German researchers believed it could be around 50,000 years old, associating it with some of the first humans who left Africa. However, Aris Poulianos, a prominent researcher, later suggested a much older origin of up to 700,000 years, igniting ongoing disputes among scientists.
The Turning Point: New Research Unveils Groundbreaking Findings
Fast forward to August 2025, when a groundbreaking study published in the Journal of Human Evolution shed new light on the mystery. Led by Christophe Falguères, the research employed uranium-series dating to determine that calcite on the skull had been accumulating for at least 277,000 years. This finding supports the idea that the skull's species may have coexisted with evolving Neanderthals and offers crucial insights into human ancestry.
What Does This Mean for Human Evolution?
The classification of the Petralona skull as Homo heidelbergensis, an extinct humanoid species, shakes the foundations of our understanding: it suggests that diverse human forms existed simultaneously. As paleoanthropologist Chris Stringer notes, the new age estimates reveal a complex tapestry of human evolution—where different species, including Neanderthals, coexisted and interacted.
A New Chapter in Our Story
The Petralona skull not only challenges established narratives but also invites further exploration into human lineage. As scientists continue to investigate, there’s no doubt that this ancient find has reignited curiosity about our origins and the many forms of humanity that once walked this Earth. The story of our evolution is far from over!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)