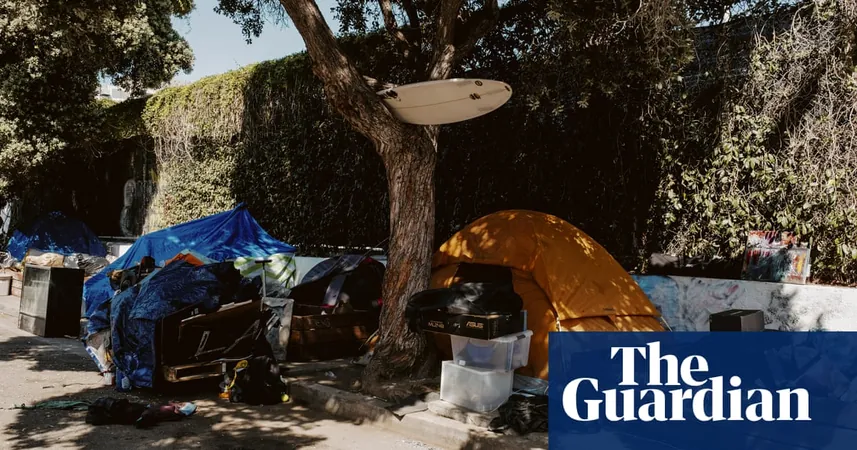

Alarming Surge in US Homelessness at the Start of 2024: What’s Driving This Crisis?
2024-12-27
Author: Jacques
A Shocking Increase in US Homelessness
A shocking report from the US Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) reveals that homelessness in the United States soared by 18% at the start of 2024. In an alarming trend, nearly 771,480 individuals were counted as unhoused during the annual tally conducted in January, surpassing the population of major cities like Seattle. This statistic equates to approximately 23 out of every 10,000 Americans living without stable housing, marking the highest figure ever recorded.
Experts believe that these numbers may fall short, as they only capture a single moment in time and overlook those temporarily staying with friends or family. This implies that the real figure could be even greater.
Impact on Families and Children
The homelessness crisis affects almost every demographic group, with a particularly concerning increase among families with children. The report revealed that nearly 150,000 children were counted as homeless in January alone, highlighting the dire situation facing youth across the nation.
Veteran Homelessness Decline
Interestingly, not all demographics are faring the same; the number of veterans experiencing homelessness saw a decline of about 8% compared to 2023, thanks to concerted funding efforts aimed directly at veteran support. Since 2009, the rate of veteran homelessness has plummeted by an impressive 55%.
Factors Driving the Crisis
The report attributes this surge in homelessness to several interconnected factors: an ongoing affordable housing crisis, rising inflation, stagnating wages, systemic racism, health emergencies, and the effects of recent natural disasters. The discontinuation of pandemic-era social protections, like the expanded child tax credit, has only exacerbated the issue.
Regional Disparities and Challenges
The situation was particularly grim for those in Hawaii, where over 5,200 individuals sought shelter in emergency facilities after devastating wildfires on Maui. Meanwhile, in various parts of the country, communities grappled with families displaced due to hurricanes and other natural disasters.
The increasing number of asylum seekers—many of whom are families—further strained local resources, although rates of unauthorized border crossings have since decreased, prompting some cities to close their migrant shelter systems.
Successful Strategies
HUD officials pointed to successful strategies implemented in cities like Dallas and Los Angeles, where initiatives aimed at expanding affordable housing have begun to yield positive results. The Dallas Street to Home Initiative and substantial investments in Los Angeles showcase what can be achieved when resources are allocated wisely.
HUD's Commitment
Adrianne Todman, HUD’s chief, emphasized the administration's commitment to tackling homelessness. "No American should face homelessness, and the Biden-Harris administration is dedicated to providing every family with the affordable, safe, and quality housing they need," she stated. While the figures are based on data from nearly a year ago, Todman reiterated the importance of evidence-based approaches to combat homelessness effectively.
Demographic Analysis
The report also provided a detailed demographic analysis of those affected by homelessness. Alarmingly, older adults aged 55 and above constituted one in every five homeless individuals. Black Americans continue to face disproportionate rates of homelessness: although they make up only 12% of the US population, they represent 32% of those unhoused.
Gender disparities within the shelter population also emerged, with about 72% of unhoused women and girls finding refuge in shelters compared to nearly 70% of men who remain unsheltered. The report noted that Black and Hispanic individuals were more likely to reside in shelter systems, while American Indians and Alaska Natives had the lowest rates of shelter usage, below 50%.
Policy Implications and Future Outlook
These findings come at a time when cities nationwide are ramping up policies aimed at addressing encampments. Following a groundbreaking Supreme Court ruling in June, local authorities are now permitted to enforce camping bans in public spaces even when shelter beds are not available. Since the ruling, over 100 cities have enacted such bans, raising further concerns about the human rights implications of these policies.
As the crisis unfolds, the urgent need for comprehensive solutions is more pressing than ever—how will the US address these alarming trends in homelessness moving forward?








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)