
Alarming Melting Trends on the Amery Ice Shelf Raise Concerns for Antarctica's Future
2025-01-20
Author: William
Overview of Melting Trends
As we head into 2025, the icy expanse of Antarctica is witnessing an unprecedented increase in melting, especially around its coastal regions. By early January 2025, extensive meltwater remained glistening atop the Amery Ice Shelf, which is located in East Antarctica, as well as along the Antarctic Peninsula. This trend raises urgent questions about future sea-level rise and the stability of the continent's ice reserves.
Satellite Observations
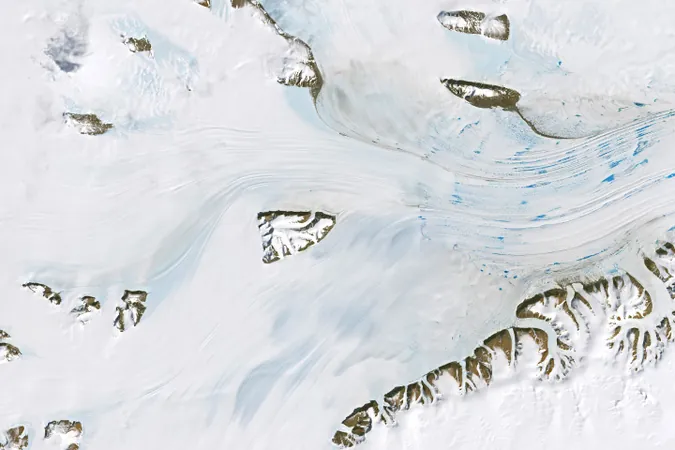
Recent satellite images captured by Landsat 8's Operational Land Imager (OLI) on January 1, 2025, illustrate a concerning scene. Glaciers such as the Lambert, Mellor, and Fisher converge near the continent’s edge, where they extend outwards, forming the Amery Ice Shelf. This ice shelf, whose southern side nears its grounding line, plays a crucial role in the dynamics of ice flow toward the ocean.
Significance of Ice Shelves
Ice shelves function as critical barriers, or 'buttresses,' that impede the flow of ice from inland glaciers into the ocean. This buffering effect is essential in slowing the discharge of glacial ice, which directly impacts global sea levels. Thick and stable ice shelves, like Amery, are best suited for this role. However, the presence of meltwater—evident in the form of blue puddles or melt ponds—can undermine these structures. When meltwater seeps through cracks, it can weaken the ice shelf, making it more vulnerable to collapse—a scenario that could exacerbate sea-level rise.
Current Melt Season Analysis
This year, the Antarctic melt season, running from November 1 to March 31, has already shown signs of widespread melting, with rising summer temperatures leading to the formation of melt ponds. Winds have further aggravated the situation by stripping away winter snow, exposing darker, more heat-absorbing ice beneath.
Research Insights
Bert Wouters, a researcher at TU Delft, notes an increase in the extent of melt ponding on the Amery Ice Shelf compared to previous seasons. He emphasizes, 'Although it’s early in the melt season, the potential for more extensive ponding remains high in the coming weeks.'
Broader Implications
Worryingly, the melting patterns observed on the Amery Ice Shelf are part of a broader transformation occurring across Antarctica. A significant melt event in mid-December 2024 resulted in an all-time record extent of melting, with satellite sensors detecting melting across over 3 percent of the entire Antarctic Ice Sheet's surface.
Outlook and Conclusions
While melt ponding typically occurs close to the grounding line of the Amery, it’s worth noting that areas nearer to the ice shelf's front maintain cooler and drier conditions, preventing similar melt pond formation. However, Wouters cautions that even minor increases in temperature could expose these regions to melt, thereby worsening the situation and leading to even more pronounced impacts on global sea levels.
The unfolding story of the Amery Ice Shelf serves as a stark reminder of the pressing challenges posed by climate change. If these trends continue, the implications could be dire, not just for Antarctica but for coastal communities around the globe. The world must pay close attention as researchers continue to monitor these dynamic and changing landscapes.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)